User Scenario vs User Journey: Differences and Uses
-
Bella Williams
- 10 min read
Experience Mapping Analysis serves as a vital tool in understanding how users engage with a product or service. By differentiating between user scenarios and user journeys, we gain meaningful insights into the customer experience. For instance, while a user scenario outlines specific situations in which a user might interact with a system, a user journey maps the complete path taken by a user, highlighting emotions, motivations, and potential pain points.
Utilizing Experience Mapping Analysis allows businesses to identify areas for improvement, leading to enhanced user satisfaction. This nuanced understanding empowers organizations to design more effective interactions, ultimately guiding users more smoothly through their experiences. By focusing on both scenarios and journeys, businesses can create tailored strategies that address real user needs.
Understanding the Core Concepts of Experience Mapping Analysis
Experience Mapping Analysis provides a structured approach to understanding user interactions and emotions throughout their journey. By identifying key touchpoints, businesses can assess how users feel at different stages, from awareness to decision-making. Recognizing these emotions is crucial as they drive customer needs and expectations. For instance, curiosity may arise during the awareness stage, while concerns could dominate the consideration phase.
To enhance this analysis, organizations should base their insights on objective data, such as survey results. Utilizing qualitative research, including interviews, can help capture authentic customer sentiments. This direct feedback will guide businesses in tailoring experiences that meet user expectations. By aligning strategies with customer emotions and needs, companies can create more effective user scenarios and journeys. Ultimately, mastering Experience Mapping Analysis can profoundly impact customer satisfaction and retention.
Defining User Scenario in Experience Mapping Analysis
In Experience Mapping Analysis, a user scenario encapsulates a specific interaction between a user and a system. This scenario outlines the context, user needs, and desired outcomes, offering a vivid picture of user behavior in particular situations. For instance, consider a user scenario that follows a customer named Sarah as she navigates an online clothing retailer’s website. Her journey highlights emotional responses and decision-making processes, which can unveil insights into potential friction points.
By mapping user scenarios, organizations can identify gaps in their user experience. This practice allows for a clearer understanding of how specific components of the service or product influence user satisfaction. For Sarah, her experience was marred by confusion in navigation and delays in delivery. Analyzing such scenarios in detail equips businesses with the knowledge to make targeted improvements, ensuring a smoother, more enjoyable user journey moving forward.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.
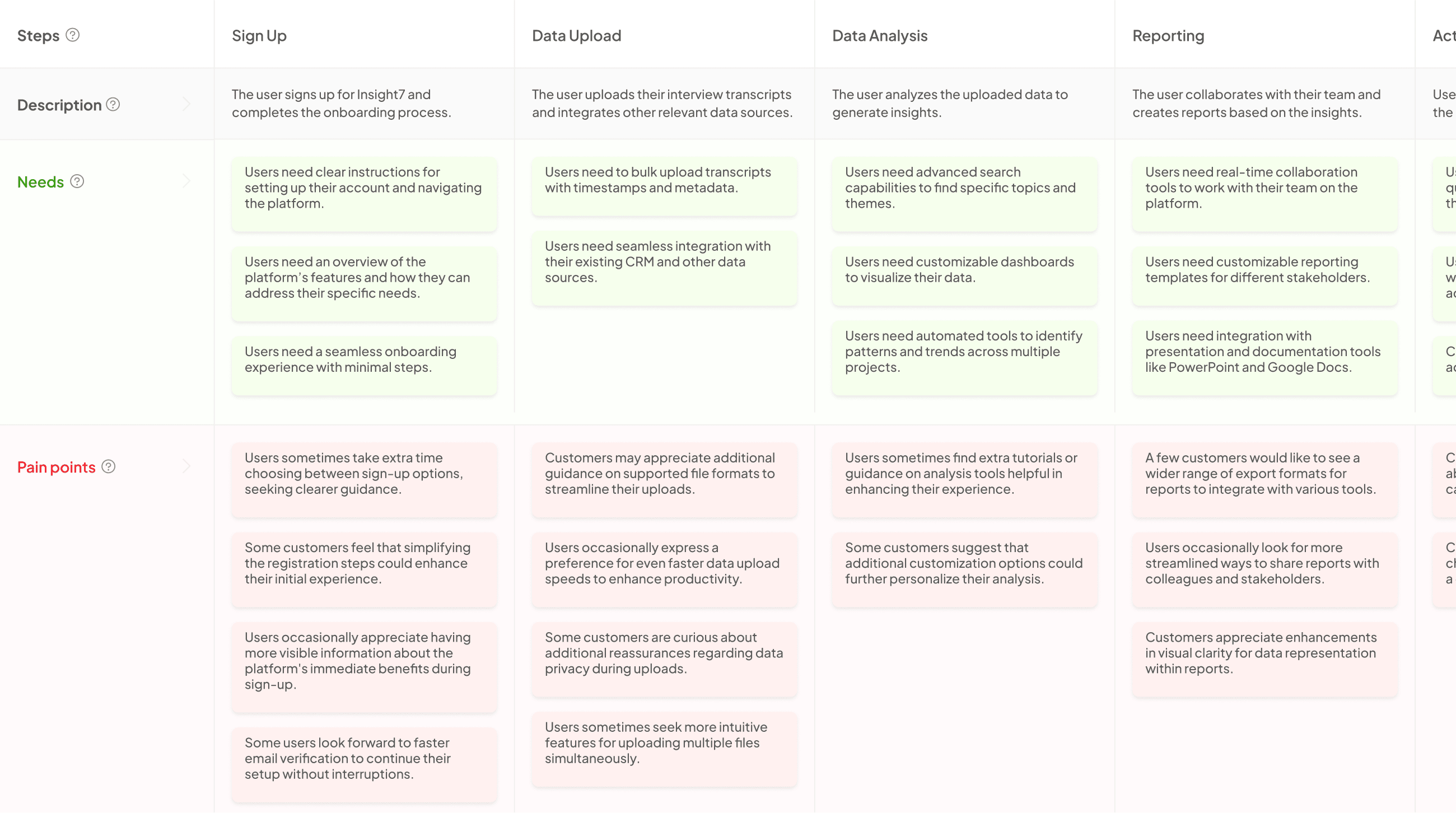
Defining User Journey in Experience Mapping Analysis
In Experience Mapping Analysis, defining the user journey is crucial for understanding how users interact with your product or service. The user journey encompasses all stages of the customer’s experience, from awareness through to purchase and post-purchase support. By mapping this journey, organizations can identify pain points and areas for improvement, ensuring that they cater effectively to user needs.
For instance, consider the fictional online retailer, FashionFusion. Sarah’s experience highlights key stages: awareness, exploration, consideration, purchase, and delivery. Analyzing Sarah’s journey, the retailer realizes improvements are necessary in website navigation, size chart accessibility, and checkout efficiency. Each of these stages reveals opportunities to enhance customer satisfaction. By focusing on the user journey, businesses can create a more seamless and engaging experience, ultimately driving customer loyalty and better performance in the competitive market.
Key Differences: User Scenario vs User Journey in Experience Mapping Analysis
In Experience Mapping Analysis, understanding the distinctions between user scenarios and user journeys is essential. User scenarios focus on specific tasks or goals of users, illustrating their motivations, needs, and interactions with a product or service. For instance, a scenario could detail Sarah’s experience when searching for a new outfit, emphasizing her thought process and decision-making.
Conversely, user journeys offer a broader perspective, capturing the entire experience over time. They document the various stages users undergo, from initial awareness to post-purchase support. Using our earlier example, Sarah’s journey captures all touchpoints with FashionFusion, highlighting pain points like website navigation and customer service barriers. Both tools are vital for identifying user needs and improving overall experiences, but they serve different purposes in guiding design and strategy. Thus, leveraging both scenarios and journeys within Experience Mapping Analysis ultimately leads to more user-centric designs.
Depth of Detail in User Scenarios and User Journeys
Understanding the depth of detail in user scenarios and user journeys is vital for any team aiming to enhance its customer experience. User scenarios describe specific situations involving a user’s interaction with a product or service, highlighting their goals and motivations. In contrast, user journeys provide a broader view, illustrating the complete path a user takes, from initial awareness through to purchase and beyond. This nuanced understanding helps identify areas for improvement, ensuring that each touchpoint aligns with user expectations.
Experience Mapping Analysis serves as a critical tool in this context. By analyzing user scenarios and journeys, teams can uncover insights about user behavior and motivations. This leads to more effective strategies for customer engagement. For instance, marketing teams can refine campaigns based on the specific touchpoints that matter most to users, whereas customer experience teams can pinpoint friction points along the journey that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Generate Journey maps, Mind maps, Bar charts and more from your data in Minutes
Scope and Context in Experience Mapping Analysis
Experience Mapping Analysis serves as a vital process for understanding user interactions and touchpoints within a specific context. By examining both user scenarios and user journeys, organizations can clarify the distinct paths users take while engaging with their products or services. This clarity helps identify critical pain points and desires, offering insights that drive improvements and innovations.
To effectively implement Experience Mapping Analysis, a few key elements should be considered. First, defining the user segments allows for tailored experiences based on user characteristics. Second, establishing clear stages of interaction provides a roadmap for analyzing user behavior at various touchpoints. Lastly, gathering qualitative and quantitative data enables a comprehensive understanding of user experiences, leading to informed decision-making. In doing so, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and achieve strategic goals.
The Uses of User Scenarios and User Journeys in Experience Mapping Analysis
User scenarios and user journeys are essential tools in experience mapping analysis, offering distinct benefits that enhance understanding of user interactions. User scenarios provide a detailed narrative of specific user actions and motivations. By focusing on a single person’s experience, these scenarios help identify pain points and areas for improvement. For instance, following Sarah’s journey on FashionFusion illuminates critical interactions that can be optimized to ensure a seamless experience.
On the other hand, user journeys present a broader overview, capturing the complete path a user takes across various touchpoints. This holistic view allows teams to spot trends and opportunities for enhancements in the overall user journey. For example, analyzing the stages Sarah went through—from awareness to consideration—reveals crucial insights that can inform design choices and support strategies. Both elements work together, enriching experience mapping analysis by providing the necessary context to create user-centered solutions that foster satisfaction and engagement.
Applying User Scenarios for Specific Problem-Solving
User scenarios play a crucial role in identifying and addressing specific problems that users encounter. By considering various contexts and motivations, they allow teams to visualize the user’s experience while pinpointing friction points in their interactions. This process is often guided by Experience Mapping Analysis, which systematically outlines user behaviors and emotions across different touchpoints.
To effectively apply user scenarios for problem-solving, consider the following steps:
- Identify user needs: Understand the core issues users face and gather insights on their expectations.
- Create detailed scenarios: Develop realistic narratives that illustrate how users interact with products or services in their daily lives.
- Map the journey: Visualize the user’s path, highlighting key moments and points of frustration that require attention.
- Analyze findings: Review the mapped experience and identify areas for improvement, making informed decisions on design and functionality.
By employing these steps, organizations can engage deeply with user experiences and enhance the overall product satisfaction.
Utilizing User Journeys for Comprehensive User Experience Insights
Utilizing user journeys provides profound insights into user experiences that can shape marketing strategies and service offerings. By employing experience mapping analysis, businesses can decode the emotions, motivations, and decision-making processes of their customers. This understanding serves as a foundation to create tailored experiences that align with customers’ desires and improve overall satisfaction.
To effectively utilize customer journey maps, businesses should focus on three crucial steps. First, integrate the journey map with key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure effectiveness. This alignment ensures that the insights directly inform improvements and amplify customer engagement. Second, conduct regular analysis sessions to revisit and refine the journeys based on changing user behaviors. Finally, collaborate cross-functionally within the organization to share findings and make holistic enhancements to services and offerings. This iterative process transforms user journeys into invaluable assets, leading to increased visits and loyal customers.
Conclusion: Synthesizing Experience Mapping Analysis Insights
To conclude, synthesizing insights from Experience Mapping Analysis reveals the distinct roles of user scenarios and user journeys. While user scenarios illustrate specific contexts and motivations, user journeys explore the broader experience over time. Both tools complement each other, enhancing our understanding of user interactions and needs.
Analyzing these insights allows organizations to create more effective strategies. By aligning user pain points and desires with their unique journeys, businesses can deliver tailored solutions and improved experiences. This approach also fosters meaningful connections with users, ensuring that their needs are continuously met throughout their engagement.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.








