Process Map vs. Journey Map: What’s Difference?
-
Bella Williams
- 10 min read
Mapping Differences between process maps and journey maps is essential for understanding how each serves unique purposes in visualizing workflows and customer interactions. A process map outlines the step-by-step operations within a business, typically focusing on efficiency, thereby offering clarity on internal processes and potential areas for improvement. In contrast, a journey map centers on the customer experience, illustrating emotions, behaviors, and needs throughout their interaction with a product or service.
By comparing these two tools, organizations can identify their distinct functions. Understanding the complexities of each type of map aids teams in refining their strategies and enhancing collaboration. This ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, ensuring a more holistic approach to both business processes and customer experiences.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.
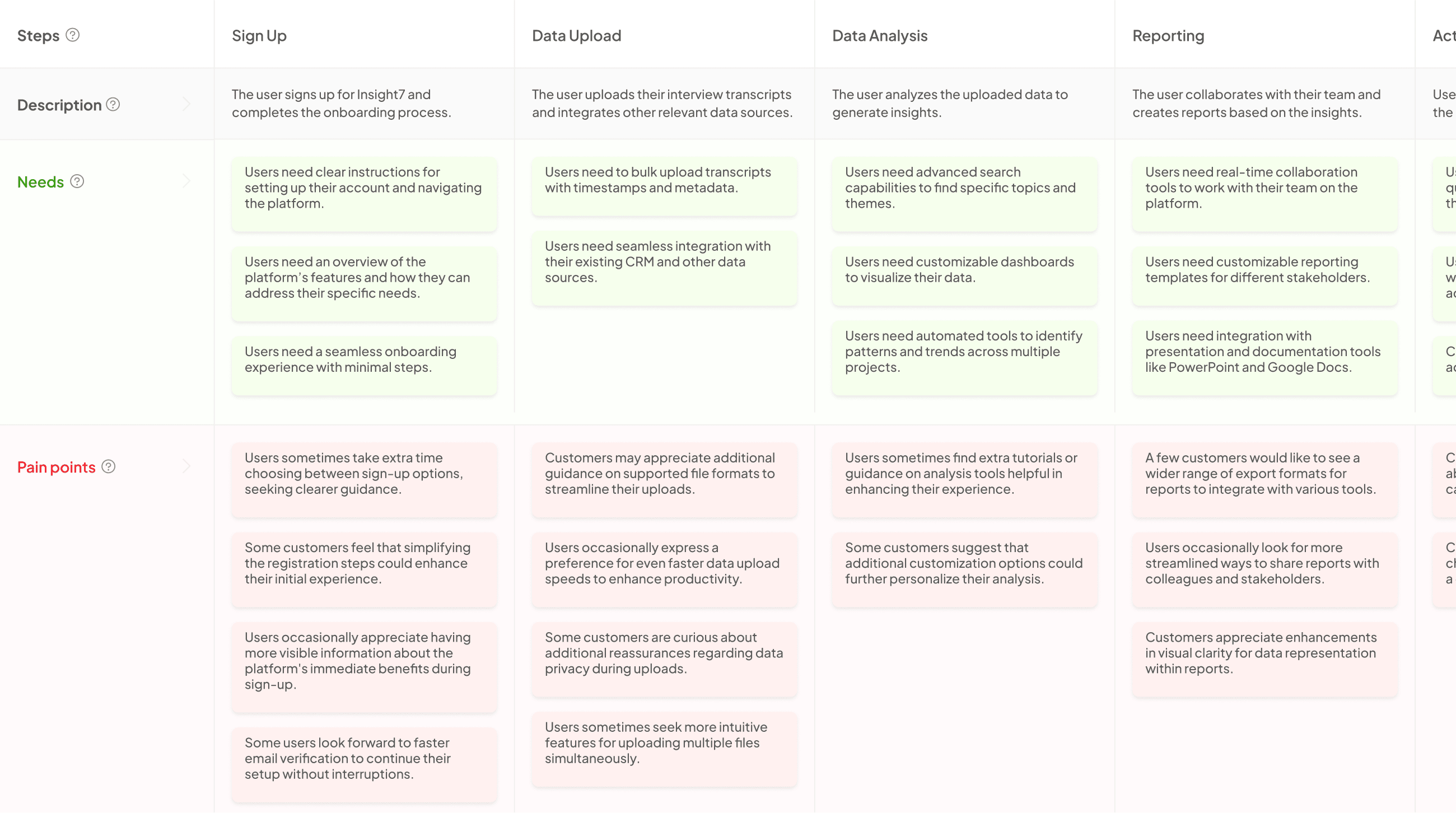
Unveiling Process Mapping Differences
In the exploration of mapping differences, it’s crucial to recognize that process maps and journey maps serve distinct purposes, despite some overlapping features. Process maps are designed to illustrate the mechanics of a workflow, showcasing the steps necessary to complete a task. They focus on efficiency and optimization, helping teams identify bottlenecks and streamline operations. Conversely, journey maps concentrate on the customer experience, capturing the emotional and experiential aspects of a customer’s interaction with a product or service.
Understanding these differences helps organizations implement targeted strategies for improvement. Process maps emphasize the steps and structure of operations, while journey maps emphasize user emotions and touchpoints, guiding marketing and customer service strategies. Embracing both approaches allows businesses to enhance efficiency and elevate customer satisfaction, creating a holistic view of the customer’s interaction from both operational and experiential perspectives.
Understanding the Basics of Process Mapping
Understanding how process mapping works is key to distinguishing it from other visualization tools, such as journey maps. At its core, process mapping involves breaking down processes into discrete steps that highlight potential areas for improvement or bottlenecks. By mapping differences, organizations can pinpoint exactly where inefficiencies occur. This structured approach allows teams to analyze workflows critically, improving clarity and alignment among stakeholders regarding specific tasks and responsibilities.
To create a process map, follow these essential steps:
- Define the Objective: Understand the purpose of mapping the process to ensure alignment with business goals.
- Identify Key Steps: Break the process into clear, sequential actions that stakeholders take from start to finish.
- Assign Roles: Clearly outline who is responsible for each step, which helps to enhance accountability.
- Visualize the Flow: Use diagrams or flowcharts to represent steps visually, making it easier for teams to understand and assess the process.
- Analyze and Improve: Review the map critically to identify inefficiencies or redundancies, enabling targeted improvements.
With this understanding and structured approach, organizations can streamline operations effectively.
Key Components of Process Maps
Understanding the key components of process maps is essential for effective communication and clarity in organizational processes. At its core, a process map visually represents the sequence of steps in a process, allowing teams to see how tasks and responsibilities align. Each component, including inputs, outputs, and decision points, plays a critical role in illustrating the flow of activities.
Another fundamental aspect is the use of symbols and notations to convey specific actions or decisions. These visual cues simplify complex information, making it easier for stakeholders to grasp the underlying processes quickly. By highlighting Mapping Differences, organizations can distinguish between how process maps and journey maps serve unique purposes in understanding customer experiences and operational efficiencies.
Generate Journey maps, Mind maps, Bar charts and more from your data in Minutes
Exploring Journey Mapping Differences
Mapping differences between process and journey maps play a crucial role in understanding customer experiences. While process maps focus on internal workflows and efficiency, journey maps emphasize the emotional and experiential aspects from the customer’s perspective. By visualizing these different elements, businesses can uncover gaps in their customer interactions and enhance overall satisfaction.
To explore these mapping differences effectively, consider the following key points:
- Perspective: Process maps generally represent a company’s internal procedures, whereas journey maps portray the customer experience.
- Components: Process maps include tasks and operations, while journey maps highlight emotions, touchpoints, and pain points.
- Purpose: The focus of process maps is to improve operational efficiency; journey maps seek to improve customer engagement and satisfaction.
Understanding these distinctions helps organizations align their strategies with customer needs, paving the way for more meaningful interactions.
The Essentials of Journey Mapping
Journey mapping focuses on visualizing the customer experience, capturing every interaction they have with a brand. It sheds light on customer emotions, motivations, and pain points throughout various stages of their buying journey. This is crucial for businesses aiming to refine their marketing strategies and enhance customer satisfaction.
Understanding the mapping differences between process maps and journey maps is essential. A process map outlines the steps in a process, often with a focus on efficiency and operations. In contrast, a journey map centers around the customer’s perspective, emphasizing their experiences and feelings. Both are valuable tools, but they serve distinct purposes. To effectively utilize journey mapping, businesses should identify customer touchpoints, gather insights from user feedback, and adjust their strategies accordingly. This continuous refinement can lead to greater customer loyalty and improved service delivery.
Unique Elements in Customer Journeys
The unique elements in customer journeys reveal valuable insights that can transform how businesses engage with their audiences. By understanding the various touchpoints in the customer experience, organizations can align their strategies more effectively. Key aspects of these journeys include emotional triggers, decision-making moments, and opportunities for personalized interactions. Each moment serves as a chance to enhance customer satisfaction, tailoring offerings to meet individual needs.
When considering mapping differences, it becomes important to differentiate the motivations behind various interactions. Customers often seek fulfillment, information, or support during their journey. By analyzing these motivations, businesses can develop targeted strategies that address specific pain points and elevate the overall experience. Ultimately, acknowledging these unique elements not only fosters better communication but also strengthens brand loyalty, creating a lasting impression that encourages return visits and ongoing engagement.
Conclusion: Mapping Differences Highlighted
In summary, mapping differences between process maps and journey maps reveals some significant insights into how businesses understand and improve customer experiences. Process maps detail the specific steps involved in a workflow, focusing on efficiency and task optimization. In contrast, journey maps emphasize the emotional and experiential aspects of the customer, portraying how they interact with a brand throughout the purchasing process.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.

Acknowledging these distinctions is essential for organizations wishing to enhance their customer engagement strategies. By combining both mapping approaches, a clearer picture emerges, allowing companies to innovate and adapt effectively to evolving customer needs. Embracing these mapping differences can lead to more informed decision-making and better overall customer satisfaction.







