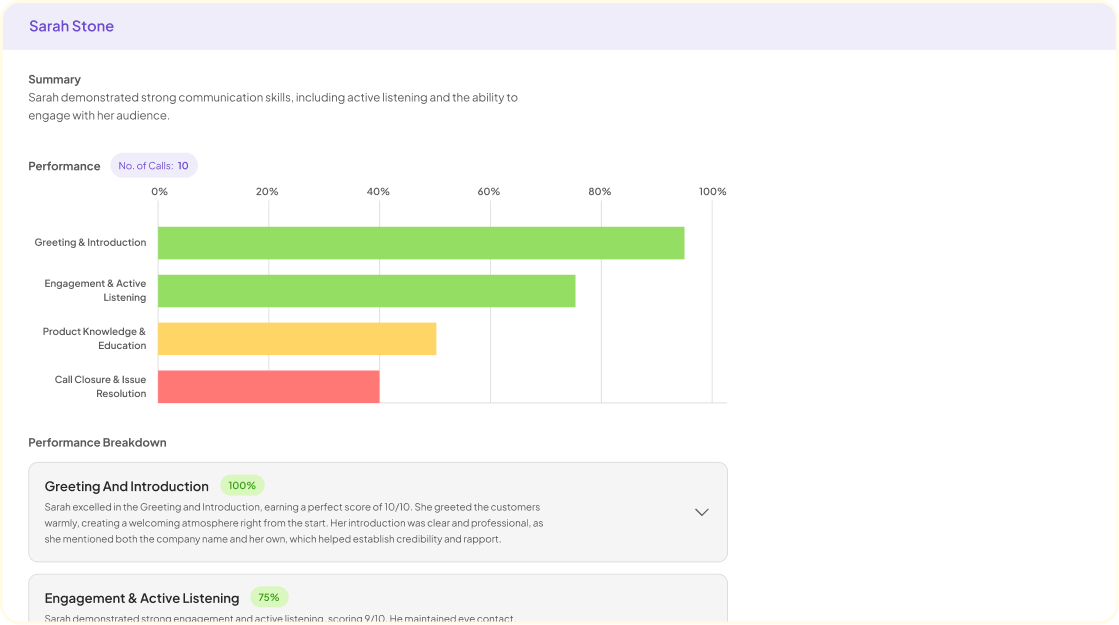
Qualitative data management is essential to navigating the complex narratives within research findings. At its core, this approach transforms raw insights from interviews, focus groups, or observations into structured and actionable information. Researchers must recognize the significance of organizing and analyzing qualitative data, as it helps uncover the underlying themes and patterns that enhance understanding.
Effective qualitative data management involves systematic coding and categorizing of responses. This process not only makes data interpretation more efficient but also ensures the integrity and reliability of findings. By implementing rigorous management practices, researchers can effectively address research questions and contribute to the broader knowledge in their respective fields. The journey from data collection to insightful reporting is crucial in creating impactful narratives that resonate with stakeholders.
Organizing Qualitative Data Effectively
Organizing qualitative data effectively is crucial for maximizing insights from research. The first step in qualitative data management involves categorizing data into specific themes or topics. By grouping similar responses, researchers can identify patterns and draw meaningful conclusions.
Next, utilizing tools like matrices can facilitate the analysis of qualitative research data. For instance, a matrix allows you to extract relevant questions from interviews and summarize key pain points experienced by participants. This method not only streamlines data but also highlights trends, making it easier to communicate findings to stakeholders. Regularly reviewing and refining your organizational strategies will ensure your qualitative data remains accessible and actionable. Ultimately, effective organization enhances the overall quality of research outcomes and supports informed decision-making.
Qualitative Data Management: Categorization and Coding
Qualitative Data Management involves systematically organizing research data to enhance understanding and analysis. One effective strategy is categorization, where data points are grouped based on shared themes or characteristics. This process not only streamlines the data but also helps in identifying patterns and insights that may otherwise be overlooked.
Coding is another essential component of qualitative data management. It involves tagging segments of text with codes that represent key ideas or concepts. This technique allows researchers to quickly reference and retrieve relevant data, facilitating deeper analysis. By categorizing and coding qualitative data, researchers can extract more meaningful insights and ultimately improve decision-making processes. Such structured management is crucial in obtaining reliable outcomes from qualitative research endeavors.
Digital Tools for Managing Qualitative Data
Digital tools have transformed qualitative data management by streamlining the process of working with complex information. These tools enable researchers to collect, organize, and analyze qualitative data more effectively than traditional methods. As a result, researchers can focus on deriving insights rather than getting bogged down in the minutiae of data management.
There are several key digital tools that enhance qualitative data management. First, transcription software helps convert interviews and focus group discussions into text quickly. Next, qualitative data analysis software offers features for coding, categorizing, and searching data efficiently. Finally, collaborative platforms allow researchers to share insights, making it easier to discuss findings and integrate feedback. Utilizing these tools effectively not only speeds up the research process but also ensures that insights are accessible and actionable. Embracing digital solutions is essential for researchers aiming to stay competitive and responsive to their audiences.
Ensuring Reliability and Validity in Qualitative Data Management
In qualitative data management, ensuring reliability and validity is essential for meaningful insights. Reliability refers to the consistency of your data, while validity pertains to the accuracy of what you're measuring. Establishing clear criteria for data collection aids in both aspects, helping researchers to create a robust framework. Utilizing standardized procedures and benchmarks can minimize discrepancies in how data is gathered and analyzed.
To enhance reliability and validity, researchers should focus on several key strategies:
Develop a Clear Framework: A structured approach outlines objectives and methodologies, reducing variance in data collection processes.
💬 Ask About This Article
Have questions? Get instant answers about this article.
Powered by Insight7Triangulation: Combining multiple sources or methods to validate findings increases confidence in the results.
Member Checking: Involve participants in reviewing findings to ensure the interpretations align with their perspectives.
Audit Trails: Keeping detailed records of decision-making processes and data can support the integrity of the research.
Continuous Reflection: Regularly evaluate your own biases and preconceptions throughout the data management process.
By implementing these strategies, researchers can enhance the quality of their qualitative data management efforts and ensure that their findings are both reliable and valid.
Techniques for Data Triangulation
Data triangulation is a crucial technique in qualitative data management, enhancing the validity and robustness of research findings. By integrating multiple sources of data, researchers can identify patterns and validate conclusions. One effective approach involves combining interviews, focus groups, and observation. Each method provides unique insights that contribute to a richer understanding of the research subject.
In addition, using different data collection methods can help in cross-verification, ensuring that the findings are consistent across various platforms. For instance, triangulating data from surveys with qualitative interviews offers depth and context, enabling researchers to capture the full picture. This multifaceted strategy not only reduces potential biases but also enriches the narrative derived from qualitative data, ultimately leading to more reliable insights. By employing these techniques, researchers can strengthen their analyses and provide compelling evidence to support their conclusions.
Using Software for Data Analysis and Interpretation
Using software for data analysis and interpretation involves harnessing technology to enhance qualitative data management. Various software tools facilitate seamless data organization, ensuring that researchers can easily retrieve and analyze their data. These tools typically include transcription capabilities, which convert recorded audio into text for detailed analysis—making patterns and themes clear. A unified platform allows you to create comparative analyses across different data sets, enabling effective insights generation.
Moreover, dashboards and analytics interfaces are integral for visualizing data outcomes in a clear and informative manner. These features help users explore relationships between variables, allowing for deeper interpretation of the data. By automating these processes, researchers save time and focus on drawing meaningful conclusions from their findings. Ultimately, employing software in qualitative research not only streamlines the data management process but also elevates the overall quality of analysis and interpretation.
Conclusion: Mastering Qualitative Data Management for Research Success
Mastering qualitative data management is essential for driving research success. By systematically organizing and analyzing qualitative data, researchers can uncover meaningful insights that guide decision-making. Effective data management allows researchers to identify patterns, themes, and significant quotes that enrich their findings, making their conclusions more robust and actionable.
Ultimately, attention to qualitative data management enhances the overall research process. Researchers can transform raw data into valuable insights, enabling a clearer understanding of participant experiences. Embracing effective data management strategies not only streamlines analysis but also fosters a culture of informed decision-making, paving the way for impactful research outcomes.
💬 Ask About This Article
Have questions? Get instant answers about this article.