User Journey Map vs. User Story Map Explained
-
Hello Insight
- 10 min read
In the intricate landscape of user experience, understanding “Journey vs. Story Mapping” is essential. Both methods guide organizations in visualizing different aspects of user interaction, yet they each serve distinct purposes. User journey maps illuminate the stages, touchpoints, and emotions a user encounters throughout their experience. Conversely, user story maps focus more on the tasks users want to accomplish, placing value on features and functionalities.
As you embark on this exploration, consider how journey mapping illustrates the customer’s complete experience, revealing pain points and opportunities for enhancement. In contrast, story mapping emphasizes actionable steps to meet user needs effectively. By grasping the nuances of each approach, you can create a more impactful user experience and foster stronger connections with your audience.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.
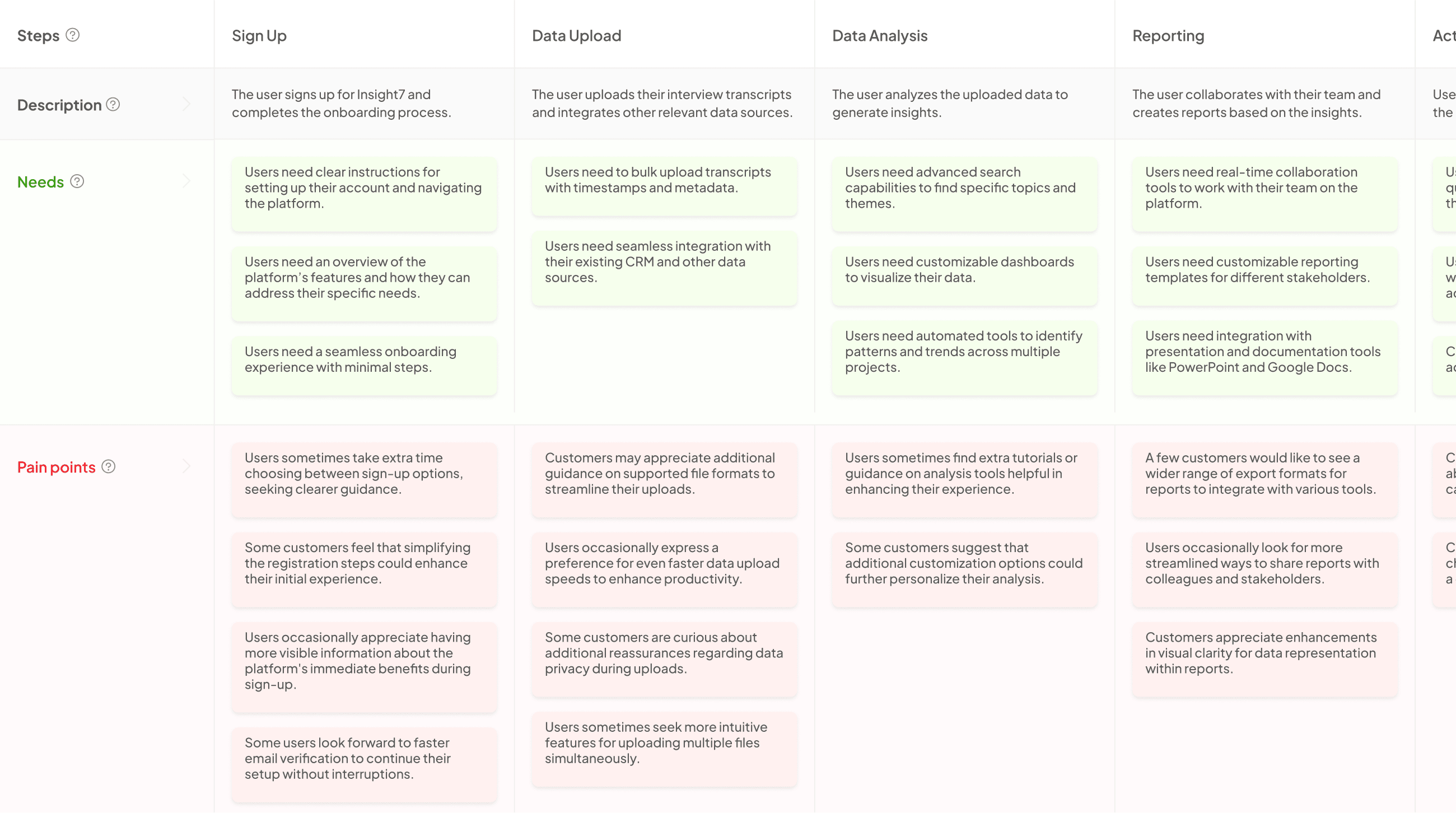
Understanding the Basics: Journey vs. Story Mapping
Understanding the fundamentals of Journey vs. Story Mapping is essential for optimizing user experiences. User journey maps focus on visualizing the complete customer experience, outlining the stages, touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities along the way. These maps emphasize how users interact with a product or service, capturing their feelings and thoughts at each stage. By mapping these elements, businesses can identify challenges and enhancement points, ultimately improving customer satisfaction.
In contrast, user story maps are more concerned with the tasks users need to complete within that journey. They break down functionalities and features into manageable units that can be developed and prioritized effectively. While journey mapping centers on the overall experience, story mapping focuses on specific user tasks. Both techniques are crucial for enhancing usability, ensuring that products align closely with user expectations. Together, they provide a comprehensive framework for understanding and improving user engagement.
Defining User Journey Maps
User journey maps provide a detailed visualization of the customer experience, tracing their journey from awareness to repurchase. This mapping technique helps businesses understand customer behaviors, emotions, and needs at each stage of their interaction. By identifying these emotional states, organizations can respond effectively at every phase, enhancing the overall customer experience.
To create an effective user journey map, it is crucial to focus on linking the different phases with corresponding customer emotions. The key phases usually include:
- Awareness: The initial stage where customers learn about a product or service.
- Interest: Here, customers start to show genuine interest.
- Consideration: Customers evaluate and compare their options before making a decision.
- Purchase: The critical moment when customers decide to buy.
By visualizing these phases, organizations can cultivate a deeper understanding of their customers, ensuring tailored marketing strategies that resonate with real user experiences. This approach ultimately bridges journey mapping with story mapping, enhancing how businesses communicate with their audience.
Defining User Story Maps
User story maps are visual tools that help teams understand and organize the various aspects of user interactions with a product. They focus on the user’s needs, goals, and the specific tasks they undertake while using the product. This approach allows teams to see the entire user journey at a glance, making it easier to identify gaps and opportunities for enhancement.
When defining a user story map, consider the core components that contribute to its effectiveness. Begin with identifying user personas, which are fictional representations of actual users. Then, outline the tasks those personas need to accomplish, mapping them visually across the timeline of their interaction with the product. Lastly, highlight the user goals that these tasks aim to achieve, establishing a clear connection between user activities and outcomes. By embracing this structured approach, organizations can effectively differentiate between journey vs. story mapping, ultimately enhancing product development and user satisfaction.
💬 Questions about User Journey Map vs. User Story Map Explained?
Our team typically responds within minutes
Generate Journey maps, Mind maps, Bar charts and more from your data in Minutes
Key Differences: Journey vs. Story Mapping
User journey mapping and story mapping serve distinct purposes in understanding user experiences. User journey mapping focuses primarily on visualizing the steps a customer takes throughout their interaction with a product or service. This approach captures various stages, touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities, offering a comprehensive view of the customer experience. On the other hand, story mapping is more about detailing the specific tasks a user needs to complete within a product. It emphasizes user stories, breaking down features into small, actionable steps that align with user goals.
In essence, while both methodologies aim to enhance user experiences, they do so from different angles. User journey mapping seeks to improve the overall journey by identifying points for enhancement. Conversely, story mapping zooms in on the functional aspects of user interaction, ensuring that each feature effectively meets user needs. Understanding these differences helps teams decide which approach aligns best with their goals, ultimately leading to a more user-centered design process.
Goals and Objectives
Setting clear goals and objectives is vital in differentiating Journey vs. Story Mapping. By understanding what you aim to achieve through these mapping techniques, you can better cater to user needs and enhance their experiences. The primary objective of a User Journey Map is to illustrate the customer’s interactions with your service throughout the entire lifecycle. This allows businesses to identify pain points, preferences, and opportunities for improvement.
Conversely, a User Story Map focuses more on the tasks users need to complete to achieve a goal. It breaks down features and functions into manageable pieces, guiding development and prioritization. Thus, aligning these objectives ensures a more comprehensive understanding of user behaviors and desired outcomes. Recognizing the differences and focusing on these goals aids in crafting a more effective strategy for improving user experiences.
Visual Representation
Visual representation plays a crucial role in the understanding of user experiences through Journey vs. Story Mapping. By creating diagrams or maps, teams can visualize customer pathways and interactions, making complex data more digestible. These visuals emphasize key moments in a user’s journey, illustrating how customers engage with a brand, product, or service over time.
Effective visual representation helps identify pain points and opportunities for enhancement. It simplifies the communication among teams, ensuring everyone is aligned on users’ experiences. By mapping both the journey and the stories behind user interactions, organizations can craft targeted strategies to address customer needs. Ultimately, these visual tools significantly contribute to improving customer satisfaction and driving engagement.
Conclusion: Journey vs. Story Mapping Summarized
In revisiting the core concepts of journey vs. story mapping, we find distinct yet complementary approaches to understanding user experiences. Journey mapping focuses on the full customer experience, detailing stages, touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities. This holistic view enables businesses to empathize with customers, improving their interactions and overall satisfaction.
On the other hand, story mapping offers a structured way to visualize user tasks and priorities. It breaks down features into manageable components, helping teams prioritize development tasks that truly matter to users. Both methods serve critical roles in enhancing user understanding and driving improvement, yet they cater to different aspects of the user experience. By integrating journey and story mapping, organizations can create richer, more compelling experiences for their users.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.

💬 Questions about User Journey Map vs. User Story Map Explained?
Our team typically responds within minutes



