Feedback Analysis: How to analyze and gain insight from customer feedback
-
Bella Williams
- 10 min read

Do you want to learn how to analyze customer feedback and discover insights and opportunities from the data? You’ve come to the right article.
Here we are going to see the right process to analyze and break down customer feedback in a way that will help the product team discover insights and opportunities to achieve product goals.
Product teams often conduct customer interviews to collect feedback on products. But many times, it’s often difficult to analyze a large set of feedback from customers.
Other times, the product team doesn’t know the correct metric to look out for in the feedback.
According to Microsoft, 52% of people around the globe believe that companies need to take action on the feedback provided by customers.
Getting customer feedback from your consumers is one thing, and analyzing it is another. Most companies collect enormous amounts of feedback from their customers, but many don’t use it to improve their products.
Feedback analysis is one of the most critical steps once you have collected your customers’ suggestions. And doing it the right way is also essential for your company’s growth.
In today’s piece, we’ll discover seven tips about customer feedback analysis.
Let’s get started.
1. Collect All Data in One Place
Now, this may first sound really obvious to you. But it’s essential for you to collect all customer feedback in one place before you start your feedback analysis.
Even if you have come across some incomplete feedback, put everything in one repository.
At first, you might avoid merging incomplete feedback with other feedback; they can unveil remarkable details.
If you are using a software or tool, export all the data in a spreadsheet or somewhere that’s visual-friendly.
Don’t dump or discard any data from the feedback you have collected as it can be a breakthrough for your company.
According to Gartner, 89% of businesses are expected to compete mainly on customer experience. And as customer experience depends on the collected feedback, you might want to think twice before discarding any customer data.
2. Categorize and Sub-Categorize Feedback
Now your customer feedback data is all-set and sitting tight in one place; it’s time to categorize it. According to your company’s nature or the feedback you have collected, organize, and sub-categorize it.
Firstly, start noticing if your data is highlighting any pattern. Then, choose a digestible theme, topic, segment, sentiment, etc. that anyone in your organization can understand to categorize the feedback.
Sorting feedback into categories will help you to see the bigger picture of what’s going on. Of course, you’ll find it hard to categorize the incomplete feedback, but it will give you a sense of what’s happening.
Lastly, break down the customer feedback data and sub-categorize it to make the picture clearer.
3. Determine how to categorize the feedback
A general rule that you can apply to help you make sense of customer feedback is to group it by:
- Type of feedback
- Feedback theme
- Feedback code
Let’s break these down.
Feedback type
Categorizing your feedback into different types is particularly helpful if you’re dealing with unclassified feedback from your customer support team or situations where customers could write anything they liked in a survey field (e.g. “Any other feedback for us?”)
Here are some categories you may find useful:
- Usability issue
- New feature request
- Bug
- User education issue
- Pricing/billing
- Generic positive (e.g. “I love your product!”)
- Generic negative (e.g. “I hate your product!”)
- Junk (this is useful for nonsense feedback like “jambopasta!”)
- Other (this is useful for feedback that’s hard to categorize. You can go back and recategorize it later as patterns emerge in the rest of the data)
Feedback theme
Breaking feedback down into themes can be useful when you’re trying to make sense of a high volume of diverse feedback, so if your data set is small (roughly speaking, 50 pieces of feedback or less) then you may not need this.
The themes you come up with will be unique to the actual feedback data you’ve received and will usually relate to aspects of the product. For example, let’s say you work on a popular product like Instagram and you’ve received a bunch of customer feedback. Your themes might look like a list of specific product features, like this:
- Photostream
- Stories
- Mentions
- Profile
This type of categorization is particularly useful when you’re working in a situation where you’re likely to have to feed your insights back to multiple teams to take action on (i.e. if you have one team that works on Stream, another on Stories, etc).
Sometimes themes can by team-related (e.g. customer support, sales, marketing) or they could be related to unmet needs that customers are experiencing. Try coming up with some themes and see if these types of categories are useful to you and the data you’re making sense of.
Feedback code
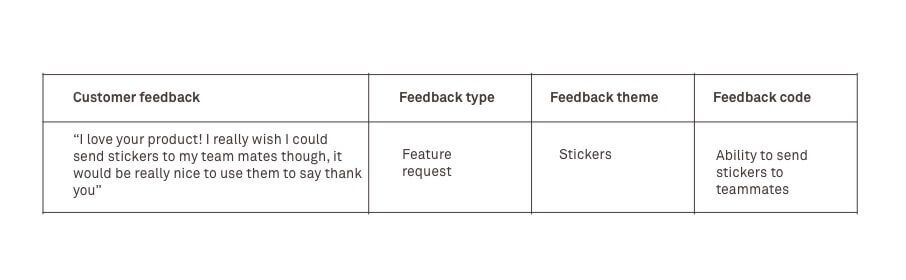
The purpose of the feedback code is to distill the raw feedback the customer has given you and rephrase it in a more concise, actionable way.
Your goal is to make the feedback code descriptive enough so that someone unfamiliar with the project can understand the point the customer was making. The feedback code should also be as concise and true to the original customer feedback as possible. Your job is to distill the feedback as objectively as possible, whether you agree with it or not.
Here’s an example:
Quick fact: Did you know that, according to Zendesk, 52% of consumers make an additional purchase after a positive customer service experience?
4. Going One Step Ahead: Searching for Root Causes
Now you have positive, neutral, and negative feedback in one place; it’s time to find the root causes behind them.
Naturally, you won’t have to break a sweat in finding causes behind positive feedback as you are already performing well in that particular section. But you need to appreciate and acknowledge the people in your team behind those positive reviews so they can keep up the excellent work.
For the neutral and negative reviews, you’ll have to find the root causes behind unsatisfied customers. For instance, you noticed that out of 1,000 negative and neutral reviews, 600 are pointing out about the delivery service. Then, your next step should be analyzing what exactly the customers are complaining about the delivery service and act accordingly.
5. Planning Actions
Once you have captured the root causes, it’s time to sketch a plan on how you would tackle the situation. For instance, it could be hiring new couriers or just planning a meeting with them and alerting them about their problems.
While planning actions, you must draw a feasible and effective plan that’s capable of at least neutralizing the negative stream you have captured in customer feedback. It would be great if you are able to generate a plan that would turn negative feedback into positive feedback as 90% of customers are influenced by positive reviews when buying something.
6. Alerting and Informing Teams
Now you have the plan; it’s about time to inform and alert your teams with the new procedures and guidelines.
Call a meeting with all the groups that require new policies and brief them with thorough and clear instructions.
Share the root causes with your teams that have made you sketch new plans and guidelines for them.
Motivate your teams to do their best to stick to the new goals. Furthermore, stay open to questions and queries from your teams to support their development.
Lastly, don’t go all hard on your teams and let them take their time to adjust.
7. Invest in Automated Tools
Analyzing thousands of customer feedback manually isn’t an efficient way to do the job. The best tip we can come up with on how to analyze customer feedback is investing in automated tools.
Automated tools will not just make your feedback analysis easy, but they will come up with great insights about it.
In minutes, you’ll see detailed reports and insights about the customer feedback data you have collected. For example, using Insight7 you are able to pick out and label different parts of each feedback in order to call them up once and create insight from that automatically.
Data analysis automated tools will help you to analyze customer feedback in less time and provide great insights.
Listening to your customers and implementing their wishes will help your business to reach new heights of success. Use these seven tips to analyze your customer feedback in the best possible way.







