Empathy Map vs. Journey Map: Key Differences
-
Hello Insight
- 10 min read
Mapping tool differences are essential for understanding how best to engage with customers. At a glance, the empathy map and the journey map serve distinct yet complementary purposes. An empathy map captures a user’s feelings, thoughts, and motivations, offering insight into their psyche. This understanding fosters deeper connections and informs product development.
Conversely, the journey map outlines the step-by-step experience a customer has with a product or service. It tracks emotions across different phases, from awareness to purchase, revealing pain points and opportunities for improvement. By recognizing these mapping tool differences, teams can tailor their strategies to provide a more holistic and satisfying customer experience.
Understanding the Basics of Mapping Tool Differences
Understanding mapping tool differences is essential when deciding between an empathy map and a journey map. Each tool serves a unique purpose in illustrating customer experiences and insights. By recognizing these distinctions, teams can better tailor their approaches to effectively meet customer needs.
Empathy maps focus primarily on expressing what a customer thinks, feels, and says. They dive deep into emotional sentiments and personal desires, highlighting pain points throughout their experience. On the other hand, journey maps provide a broader view of the entire process a customer undergoes. They break down interactions at various stages, outlining touchpoints and feedback in a more structured format. By understanding these mapping tool differences, organizations can choose the appropriate method to gain valuable insights and enhance their overall strategy.
Defining Empathy Maps
Empathy maps serve as valuable tools for understanding customers on a deeper emotional level. By visually representing the thoughts, feelings, and needs of customers, these maps enable businesses to gain insights into the customer experience. Through this understanding, organizations can tailor their strategies to meet user expectations effectively and enhance overall satisfaction.
These maps focus on four key areas: ‘Says’, ‘Thinks’, ‘Does’, and ‘Feels’. Each quadrant captures different aspects of the customer experience. The ‘Says’ section records direct customer quotes, illustrating their beliefs and desires. Meanwhile, ‘Thinks’ captures their internal thoughts that may not be vocalized. The ‘Does’ quadrant outlines the customer’s actions during their journey, while ‘Feels’ dives into their emotional state. Together, these elements provide a comprehensive view of the customer experience, facilitating the development of targeted strategies that address specific needs. By utilizing empathy maps alongside journey maps, businesses can create a holistic understanding of their customers.
Exploring Journey Maps
Journey maps serve as invaluable tools for visualizing the customer experience across various stages of their interaction with a brand. By mapping out steps such as awareness, exploration, consideration, purchase, and post-purchase support, organizations can identify pain points and areas for improvement. This structured approach allows businesses to empathize with their customers, ultimately driving better engagement and satisfaction.
Moreover, understanding the distinct mapping tool differences between journey maps and empathy maps is crucial. While empathy maps focus on understanding users’ feelings and motivations, journey maps delve into the actual experiences and challenges faced during interactions. By integrating insights from both tools, businesses can craft more holistic strategies that prioritize customer needs. This comprehensive perspective not only optimizes the customer experience but also leads to enhanced overall performance.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.
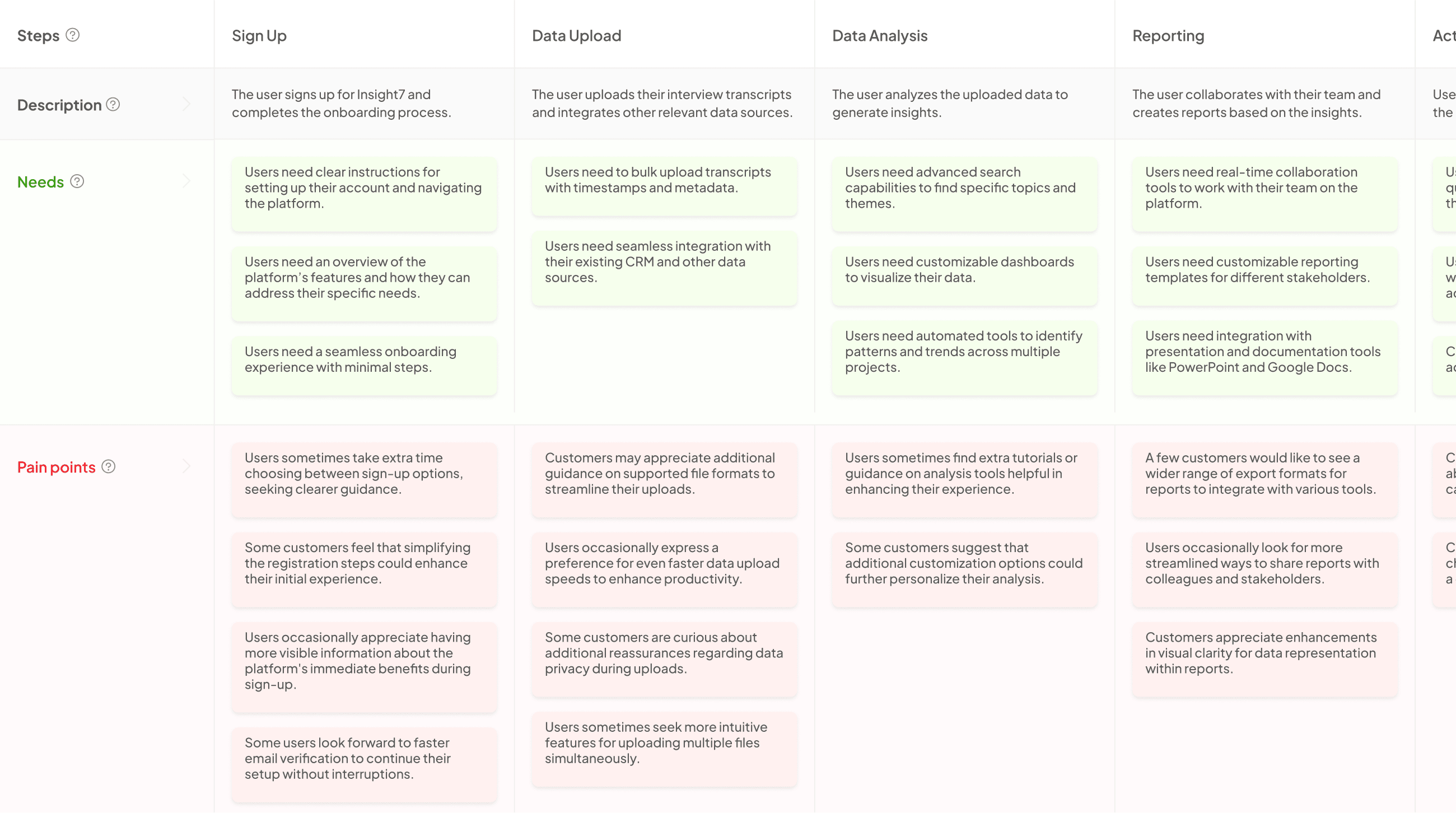
Mapping Tool Differences: Key Components
Understanding the key components of each mapping tool highlights the mapping tool differences between empathy maps and journey maps. Empathy maps focus primarily on understanding the user’s thoughts and feelings, capturing their emotions, pain points, and desires. This insight encourages a deeper connection with the users, allowing teams to consider their motivations and experiences.
In contrast, journey maps illustrate the entire user experience across various touchpoints. By analyzing customer interactions with a product or service, journey maps help identify opportunities for improvement. They outline the stages users go through, enabling teams to pinpoint where users may encounter challenges or feel satisfied. Recognizing these differences allows businesses to choose the appropriate mapping tool based on their specific goals and the insights they wish to gain.
Core Elements of an Empathy Map
An empathy map serves as a visual tool to capture essential insights about customer emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. Core elements of an empathy map include understanding what customers say, think, feel, and do. By examining these aspects, teams can create a comprehensive view of the customer, which aids in identifying their pain points and motivations. This empathetic approach ensures that businesses stay aligned with customer needs throughout the development process.
💬 Questions about Empathy Map vs. Journey Map: Key Differences?
Our team typically responds within minutes
The first key element is “Say,” which captures direct customer quotes or feedback. Next is “Think,” addressing what customers consider important or concerning, often unspoken thoughts. The “Feel” section dives into the emotional landscape, revealing fears or joys, while “Do” reflects customers’ actions in relation to your product or service. Together, these elements enable organizations to effectively tailor their strategies and respond to customer emotions more accurately. Understanding these core elements dramatically differentiates an empathy map from other mapping tools.
Essential Elements of a Journey Map
A well-constructed journey map is integral to understanding customer interactions and experiences. It typically encompasses several essential elements that differentiate it from other mapping tools. The first crucial component is the identification of touchpoints, which are moments when a customer interacts with your brand. Mapping these touchpoints helps visualize customer paths and highlights key areas for improvement.
Another vital element is the emotional journey of the customer. Understanding how customers feel at each stage is instrumental in developing strategies that address their needs and emotions. Additionally, insights gathered from customer feedback play a significant role in shaping the journey map. This data informs businesses about pain points and opportunities for enhancement. By mapping these differences, organizations can tailor their approaches, ensuring customers have the best possible experience throughout their journey.
Mapping Tool Differences in Application
When comparing the application of empathy maps and journey maps, it’s essential to understand their unique functionalities. Empathy maps focus on understanding users’ feelings, thoughts, and behaviors, making them a valuable tool for teams looking to build emotional connections with their audience. They capture insights in a simplified, visual format that prompts discussion and provides depth to user personas.
Generate Journey maps, Mind maps, Bar charts and more from your data in Minutes
On the other hand, journey maps illustrate the entire experience of a user interacting with a service or product. They outline each touchpoint and highlight pain points along the way, helping teams identify areas for improvement. This makes journey maps instrumental in strategizing enhancements and delivering seamless user experiences. While both mapping tools serve distinct purposes, understanding the mapping tool differences in application can empower teams to choose the most effective approach for their specific needs.
When to Use Empathy Maps
Empathy maps are an invaluable tool when you need to understand and visualize your customers’ emotions, thoughts, and behaviors better. They can be especially useful during the early stages of product development, where understanding user perspectives plays a critical role. This mapping tool can illuminate the complex motivations behind customer actions, helping teams create more effective solutions tailored to user needs. When you’re seeking to truly grasp how your target audience feels, empathy maps become a guiding star.
You may want to utilize empathy maps in various situations, particularly when launching new products, embarking on service enhancements, or refining user experiences. Understanding the nuances of customer emotions can lead to more meaningful engagement strategies. Additionally, empathy maps are effective for cross-departmental collaboration, as they help different teams align on customer insights. By mapping user experiences and emotions, your team can identify key areas for improvement, fostering innovation and enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
Ideal Scenarios for Journey Maps
In ideal scenarios for journey maps, they effectively illuminate each touchpoint a customer experiences with a brand. For instance, a fictional clothing retailer, FashionFusion, can use a journey map to identify pain points in Sarah’s shopping experience. Starting from her initial awareness through an online ad, the journey map outlines how Sarah navigates the website and her struggles with product filtering. This visual representation highlights where the business should enhance its website design and navigation features.
Another effective scenario occurs during product development. By mapping out the customer journey, a team can capture the entire experience from product consideration through delivery and support. Observations about Sarah’s difficulties with checkout and tracking ensure that future updates focus on improving areas that frustrate customers. Hence, customer journey maps serve as valuable tools for identifying actionable insights and fostering customer-centric policies, showcasing the mapping tool differences when compared to empathy maps that delve deeper into feelings and motivations rather than the specific actions taken.
Conclusion: Mapping Tool Differences and Their Impact on Design Strategy
Understanding the mapping tool differences profoundly affects design strategies. The empathy map focuses on understanding the emotional and psychological factors that drive customer experiences. This tool is particularly useful in creating a deep connection with users by uncovering their needs and frustrations. In contrast, the customer journey map charts the actual steps users take, highlighting interactions across various touchpoints. This map is invaluable for identifying pain points and optimizing the overall customer experience.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.

By integrating insights from both tools, teams can develop a comprehensive approach to design strategy. Sharing the insights gained from the customer journey map across departments fosters collaboration and ensures everyone aligns with the user’s perspective. This collective knowledge enhances marketing strategies and supports effective decision-making processes. A deep understanding of mapping tool differences leads to more thoughtful and user-centric design strategies.
💬 Questions about Empathy Map vs. Journey Map: Key Differences?
Our team typically responds within minutes



