In-depth analysis of qualitative study methods reveals a profound understanding of human behavior and societal phenomena. When researchers embark on a qualitative study, they often seek to delve into the intricate narratives that shape people's experiences and perceptions. By engaging with participants through interviews and focus groups, researchers gather rich, detailed data that go beyond mere numbers.
Qualitative methods are essential when exploring complex subjects, as they allow for flexibility and adaptability. These methods can capture emotions, motivations, and cultural contexts, providing depth to the research findings. Through careful data collection and analysis, these studies can uncover patterns, themes, and insights that are vital for understanding the subject matter thoroughly. This introduction lays the foundation for a detailed exploration of a qualitative study, highlighting its unique value in generating meaningful insights.
Understanding the Basics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research serves as a rich avenue for understanding human experiences and behavior through in-depth analysis. It delves into the complexities of the social world, aiming to grasp the subjective experiences of participants rather than just numerical data. This approach often involves methods such as interviews, focus groups, and observations, allowing researchers to uncover underlying motivations and emotions.
The significance of qualitative research lies in its ability to generate detailed narratives that highlight people's thoughts and feelings. By translating these insights into actionable information, stakeholders can make informed decisions. This research style is essential for exploring phenomena that are not easily quantifiable, such as cultural dynamics and individual perceptions. Ultimately, understanding the basics of qualitative research equips researchers with the tools necessary to explore intricate human behaviors and the context in which they occur.
What is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research emphasizes understanding human behavior and experiences through in-depth analysis. It goes beyond mere numbers, focusing instead on the meanings that individuals attribute to their experiences. This type of research often employs methods like interviews, focus groups, and participant observations to gather rich, descriptive data. By exploring a topic in more depth, qualitative research reveals underlying emotions and motivations that cannot be captured through quantitative measures.
Through iterative analysis, researchers can identify patterns or themes within the data, providing valuable insights. This is particularly useful in understanding complex phenomena where emotions or social contexts play a significant role. The goal is to develop a nuanced understanding of how individuals perceive and interact with their environments. This in-depth analysis ultimately informs strategies and solutions tailored to specific human experiences, making qualitative research a vital component of comprehensive studies.
Key Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by its focus on understanding the complexities of human behavior and social phenomena. In-depth analysis is a vital aspect, allowing researchers to explore the nuances of participants' perspectives. This approach seeks rich, descriptive data rather than mere numbers, emphasizing the importance of context in understanding a given situation.
Another key characteristic is flexibility in data collection methods, including interviews, focus groups, and observations. These techniques enable researchers to engage deeply with participants, fostering a natural dialogue that can reveal insights not readily captured through quantitative methods. Additionally, qualitative research often employs iterative processes, where findings inform subsequent data collection, enhancing depth and relevance. By prioritizing participant experiences, qualitative research can generate profound insights that inform decision-making and strategy development in various fields.
In-depth Analysis: Exploring a Case Study
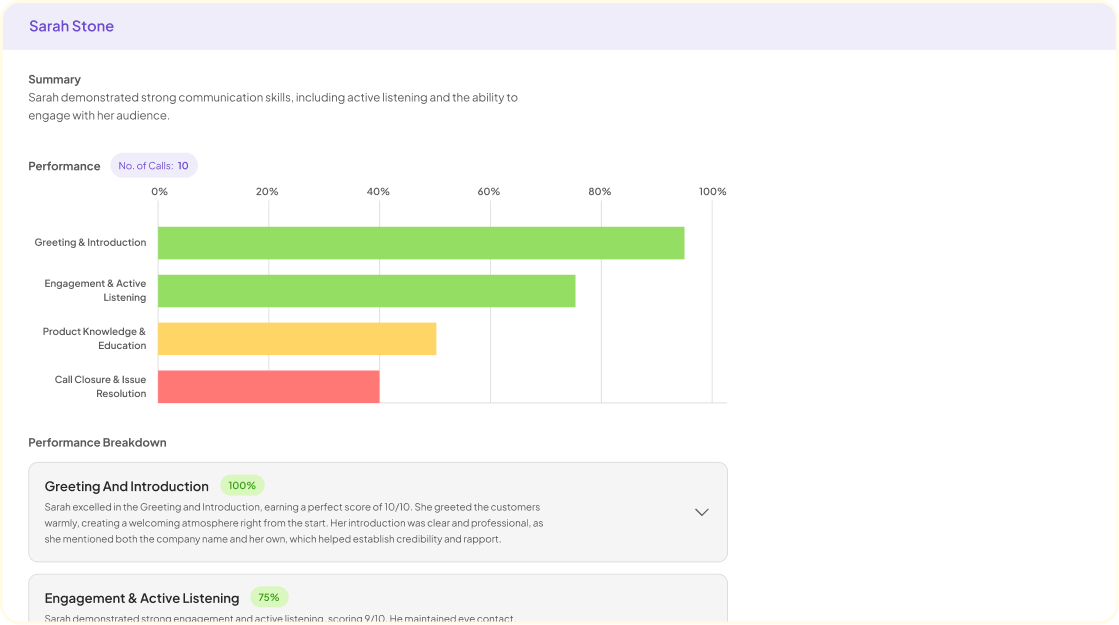
In-depth Analysis involves a careful examination of qualitative data through specific case studies. This process allows researchers to identify key themes and insights that emerge from customer interviews and interactions. By digging deep into these individual experiences, we can chart pain points, desires, and evidence that substantiate various trends within the data.
A case study can encompass various layers. First, it captures direct quotes from participants, providing tangible evidence of their emotions and motivations. Next, it summarizes the findings into succinct insights that reveal overarching patterns across multiple calls or interviews. Finally, this structured approach enables any team member to engage with the data comprehensively, formulating subsequent questions and directions for further exploration. Through this in-depth analysis, researchers not only enrich their understanding but also inform strategies that truly resonate with their audience's needs.
Selecting a Suitable Qualitative Study Example
Choosing a suitable qualitative study example requires thoughtful consideration of various factors. Begin by identifying the core research questions that guide your inquiry. This initial step narrows your focus, ensuring the selected example aligns with your objectives. Look for studies that delve into complex behaviors, emotions, or experiences, offering a rich narrative for an in-depth analysis.
💬 Ask About This Article
Have questions? Get instant answers about this article.
Additionally, evaluate the methodological rigor of potential examples. Examine the data collection techniques used, such as interviews or focus groups, as these influence the depth of insights. Consider the diversity of participants in the study to ensure a comprehensive understanding. Lastly, reflect on the findings and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in the field. By systematically applying these criteria, you can confidently select a qualitative study example that resonates with your research goals.
Methods and Techniques Used for In-depth Analysis
In-depth analysis requires an array of methods and techniques designed to elicit rich and nuanced insights. First and foremost, qualitative data collection methods such as interviews and focus groups provide an intimate understanding of participant experiences. These techniques allow researchers to explore complex emotions and perceptions, offering a deeper view than quantitative methods alone.
Next, thematic analysis is often employed to identify patterns and themes within the data. This process involves coding the data, organizing it into categories, and interpreting those categories to uncover underlying meanings. Furthermore, triangulation enhances the credibility of findings by involving multiple data sources or perspectives, ensuring a well-rounded analysis. By applying these methods, researchers can effectively transform raw data into actionable insights, ultimately driving strategic decision-making. Each technique brings its unique strengths, collectively enriching the in-depth analysis process.
Analyzing Data and Drawing Conclusions from the Study
In-depth analysis is crucial in interpreting qualitative data from a study. This process begins by organizing the collected information into themes or categories, allowing researchers to identify recurring patterns. As these themes emerge, they provide insightful narratives about the participants' experiences and perspectives. By examining the data closely, researchers can discern underlying motivations and emotions, contributing to a fuller understanding of the subject matter.
Drawing meaningful conclusions from the analysis involves synthesizing these themes into coherent insights. Researchers must consider the broader implications of their findings, reflecting on how they relate to existing literature and theory. This reflective practice not only strengthens the study's credibility but also ensures that the conclusions drawn are both relevant and applicable to real-world contexts. By engaging in this detailed process, researchers contribute valuable knowledge that can inform future research and practical applications.
In-depth Analysis of Findings and Interpretations
An in-depth analysis of findings and interpretations involves a systematic examination of the data collected during a qualitative study. This process allows researchers to identify recurring themes, patterns, and insights that can inform future decision-making and strategy development. By synthesizing the rich, qualitative data, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions that reflect participants' experiences and perspectives. Each piece of feedback gathered serves as a crucial item within the larger narrative, helping stakeholders understand the underlying motivations and needs of the participants.
To achieve a comprehensive understanding, researchers can consider several key components: first, identifying prevalent themes across the data enhances clarity and direction. Second, distilling quotes and insights from respondents contextualizes the findings, presenting them in a relatable manner. Lastly, connecting these insights to the specific research objectives ensures that the analysis remains relevant and actionable. The ultimate goal of this in-depth analysis is to transform qualitative data into valuable insights that can guide effective strategies and future research endeavors.
Challenges and Considerations in Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis presents unique challenges that researchers must navigate to achieve meaningful insights. One primary hurdle is the subjective nature of data interpretation. Researchers can bring their biases into the analysis process, potentially skewing results. This highlights the importance of maintaining objectivity throughout the study. Additionally, managing vast amounts of qualitative data can be overwhelming and time-consuming, leading to potential delays in obtaining actionable insights.
Another significant consideration involves the need for methodological rigor. Ensuring data credibility requires selecting appropriate analysis techniques that align with research objectives. This complexity can deter researchers less familiar with qualitative methods. Moreover, the dynamic nature of human experiences means that results may vary significantly across different contexts. In-depth analysis requires a delicate balance between thorough exploration of data while being cautious about overgeneralization. As researchers engage with qualitative data, understanding these challenges will aid in producing robust, actionable findings.
Conclusion: In-depth Analysis of Qualitative Study Outcomes
The qualitative study outcomes reveal essential insights gathered through participant conversations. An in-depth analysis of these interviews illuminates recurring themes such as resource allocation and feedback. These findings underscore the value of qualitative research in identifying significant patterns that may not surface in quantitative studies.
Moreover, the ability to draw direct quotes from participants adds depth to the understanding of their experiences. This approach enriches the analysis, showcasing individual perspectives within a broader context. Ultimately, this type of analysis highlights the importance of listening to voices that shape our understanding of complex issues.
💬 Ask About This Article
Have questions? Get instant answers about this article.