Ethical Data Trust serves as the cornerstone for building privacy-centric strategies in today’s data-driven world. Organizations face increasing pressure to protect individual privacy while still utilizing data to drive engagement and innovation. By embedding ethical principles into data practices, companies can cultivate a foundation of trust, respecting consumer rights and fostering transparency in their operations.
Understanding the significance of Ethical Data Trust goes beyond compliance; it reflects a commitment to prioritizing user privacy. By prioritizing transparency and integrating user-centric measures, organizations can create more empowering experiences. The path to succeeding in this endeavor lies in actively designing processes that prioritize the individual's rights while balancing the need for valuable insights.
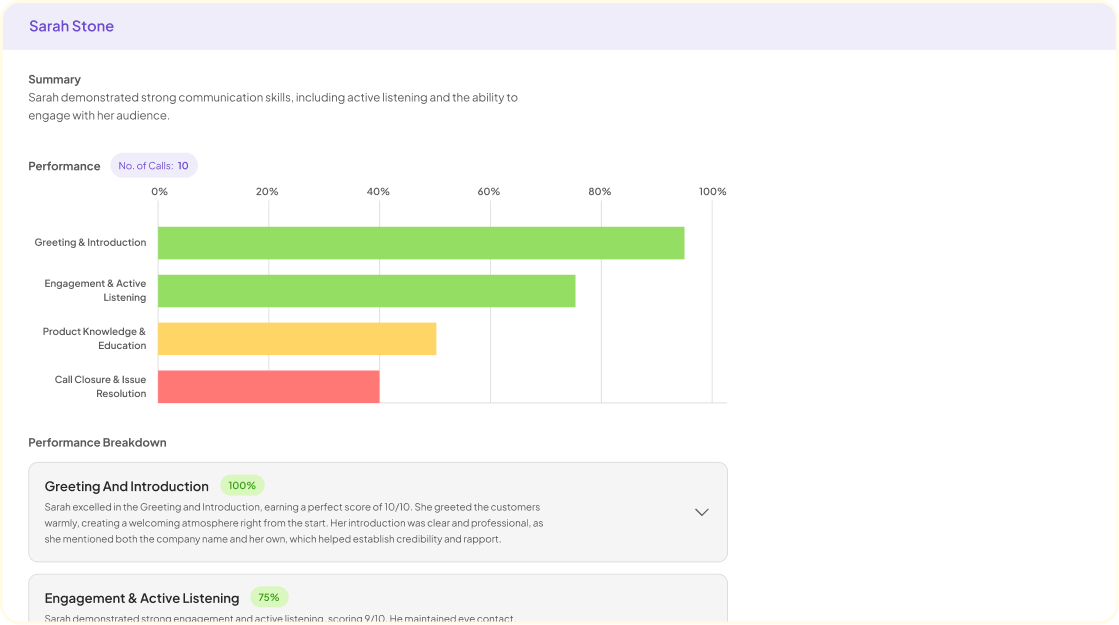
Analyze & Evaluate Calls. At Scale.

Designing Privacy-Centric Strategies through Ethical Data Trust
Designing privacy-centric strategies through ethical data trust involves creating a framework that prioritizes user privacy while fostering transparent data practices. Establishing ethical data trust requires an understanding of the responsibilities organizations have towards their users. The central idea is to create systems where individuals feel safe sharing their data, knowing it is handled with care and respect.
To achieve this, organizations can focus on core principles such as transparency and user-centric privacy measures. Transparency entails openly communicating how data is collected, used, and shared, thereby building trust with users. Additionally, implementing privacy measures designed around user needs will enhance their confidence in your data practices. By embedding these principles into the organization’s culture, companies can design effective strategies that not only protect user data but also promote long-term trust.
Core Principles of Ethical Data Trust
Ethical Data Trust is built on principles that prioritize the rights and privacy of individuals while fostering responsible data use. Transparency and openness form the foundation of this trust. Organizations must actively communicate their data practices, ensuring users understand how their information is collected, stored, and utilized. This openness not only builds confidence but also empowers users to make informed decisions regarding their data.
User-centric privacy measures further enhance Ethical Data Trust by tailoring strategies to meet individual needs and preferences. Implementing robust data protection mechanisms, such as encryption and access controls, safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access. Simultaneously, involving users in the data management process cultivates a sense of partnership, aligning organizational objectives with user interests. By prioritizing these core principles, organizations can create a sustainable model that resonates with privacy-conscious consumers while cultivating a trusting relationship built on ethical standards.
- Transparency and Openness
Transparency and openness are foundational to fostering an Ethical Data Trust. By providing clear insights into data handling practices, organizations can build confidence among users. When data practices are transparent, users feel more secure, knowing how their information is being used or stored. Openness invites critical dialogue, encouraging feedback and trust between consumers and businesses.
Crucial elements that support transparency include providing easy-to-understand privacy policies and ensuring clear communication regarding data collection purposes. By making this information accessible, organizations demonstrate their commitment to ethical practices. Furthermore, regular updates and personal data reviews empower users, reinforcing their agency in the data-sharing process. Together, transparency and openness are not just regulatory necessities; they are essential strategies that enhance credibility and foster long-term trust, creating an environment where data can be managed ethically and responsibly.
- User-Centric Privacy Measures
User-centric privacy measures prioritize individuals in the design of data strategies, ensuring their privacy is respected and upheld. Organizations should foster a deep understanding of users’ concerns related to data protection. Recognizing these concerns builds trust and enhances user experience, laying the groundwork for ethical data trust.
To implement effective user-centric privacy measures, organizations should focus on three key areas: transparency, consent, and security. First, transparency involves clear communication about data collection and usage, ensuring users are well-informed about their data rights. Next, obtaining explicit consent before collecting personal data reinforces user autonomy. Finally, robust security measures must be established to protect user data from unauthorized access, reinforcing their confidence in data handling practices. By incorporating these principles, organizations can create a privacy-centric environment that resonates with users and strengthens ethical data trust.
Steps to Implement Ethical Data Trust in Your Organization
To implement Ethical Data Trust in your organization, begin by conducting a Privacy Impact Assessment. This step enables you to identify potential risks associated with data collection and usage. By thoroughly understanding these risks, you can adopt strategies that enhance data privacy and user trust.
Next, embed Privacy by Design principles into your processes from the outset. This proactive approach ensures that privacy considerations are integrated into every aspect of data handling, rather than being an afterthought. Your organization should prioritize transparency and user control, which fosters a culture of trust.
Finally, establish ongoing monitoring and governance to ensure compliance with privacy policies. Regular reviews and updates to your strategies will help mitigate risks and adapt to evolving regulations. Emphasizing these steps will deepen your organization’s commitment to ethical data practices and build a robust foundation of trust.
- Step 1: Conduct a Privacy Impact Assessment
Understanding the importance of a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) is crucial for establishing Ethical Data Trust within your organization. A PIA serves as a foundational step in identifying and mitigating any potential privacy risks associated with data handling practices. Through a systematic evaluation of how personal data is collected, used, and protected, organizations can ensure that they are compliant with legal requirements and uphold best practices in privacy.
To effectively conduct a Privacy Impact Assessment, consider the following steps:
Identify the Data Being Collected: Begin by clearly documenting what personal data is collected, the purpose of its collection, and the intended uses. This clarity establishes a strong foundation for ethical practices.
Analyze Risks and Impacts: Evaluate how the collected data may affect individual privacy rights. Identify potential risks and their implications to ensure any hedges against misuse are in place.
Implement Mitigation Strategies: Develop strategies to address identified risks. This can include encryption, data minimization, and strict access controls to bolster privacy protections.
Document Findings: Keep a detailed record of the PIA process and its outcomes. This documentation is valuable for compliance purposes and can establish trust with stakeholders and customers.
Following these steps will enhance your organization's commitment to ethical data practices and build a stronger Ethical Data Trust.
- Step 2: Embed Privacy by Design Principles
Embedding Privacy by Design principles is crucial for fostering an Ethical Data Trust. By incorporating privacy at the initial stages of project and product development, organizations can proactively address potential privacy risks. This approach flips the conventional model, ensuring that privacy is not just an afterthought but a foundational component of systems and processes.
To effectively integrate these principles, organizations should focus on the following key areas: 1. Proactive Design: Anticipate privacy concerns early to mitigate risks before they materialize. 2. Default Settings: Implement default configurations that prioritize user privacy, simplifying choices for users. 3. User-Centric Transparency: Clearly communicate how data is collected, used, and protected, fostering trust and accountability. 4. Inclusion of Stakeholders: Engage users and stakeholders in the design process to ensure their privacy needs are met. By aligning systems with these principles, organizations can reinforce an Ethical Data Trust, promoting a culture of respect and integrity in data management.
- Step 3: Establish Ongoing Monitoring and Governance
Continuous oversight is essential for fostering an Ethical Data Trust culture within an organization. Businesses must establish frameworks that monitor data usage, ensuring compliance with ethical standards while respecting user privacy. This ongoing supervision is crucial in identifying potential risks and adapting to evolving regulatory landscapes. The governance structure should incorporate regular audits, reporting standards, and stakeholder engagement, which cultivates transparency and accountability.
Additionally, it's important to create responsive feedback mechanisms that reflect the concerns of users. Stakeholders must have avenues to voice their opinions on data practices, creating a dynamic relationship that strengthens trust. By maintaining robust governance around data practices, organizations can adjust their strategies in real time, promoting an Ethical Data Trust that not only meets regulatory standards but also aligns with the expectations and privacy of users.
Extract insights from interviews, calls, surveys and reviews for insights in minutes
Tools for Building Privacy-Centric Data Strategies
Building effective privacy-centric data strategies requires an understanding of the tools available for fostering Ethical Data Trust. Several platforms can empower organizations to uphold robust data privacy standards while delivering meaningful insights. By utilizing these tools, businesses can effectively align their data practices with privacy regulations, ensuring compliance and protecting user trust.
Among the essential tools are data privacy platforms like Privitar, which specializes in safeguarding sensitive information without compromising analytical capabilities. OneTrust offers comprehensive data governance, enhancing transparency in privacy practices, while BigID focuses on data intelligence to identify and manage privacy challenges effectively. Lastly, IBM Watson provides AI-powered solutions that not only enhance privacy but also streamline data handling. These tools help organizations build a framework centered on Ethical Data Trust, ultimately fostering a culture of accountability and ethical data management.
insight7: Enhancing Ethical Data Practices
Ethical data practices serve as the backbone for fostering Ethical Data Trust and ensuring privacy-centric data strategies. Organizations must focus on transparency and accountability in their data handling processes. By openly communicating how data is collected, stored, and used, they can nurture a culture of trust among users. This involves implementing robust measures that empower individuals to exercise control over their own data, leading to a stronger relationship between companies and their customers.
To enhance ethical data practices, organizations can take several actionable steps. First, conducting a thorough privacy impact assessment allows teams to identify potential risks associated with data handling. Next, embedding privacy by design principles ensures that privacy considerations are integrated throughout the lifecycle of data management processes. Finally, establishing ongoing monitoring and governance practices promotes continual improvement, helping organizations stay compliant while building lasting Ethical Data Trust.
Additional Tools
In today's digital age, organizations must prioritize tools that reinforce their commitment to ethical data trust. By exploring various technologies, businesses can enhance their privacy-centric data strategies significantly. A few noteworthy tools include Privitar, OneTrust, BigID, and IBM Watson, each designed to handle unique data protection challenges.
Privitar focuses on enabling data privacy through advanced anonymization techniques. Its solutions empower organizations to share data while safeguarding sensitive information. OneTrust provides a robust platform for managing privacy, security, and data governance; its comprehensive features help maintain compliance with regulations. BigID specializes in data intelligence, offering insights into data classification and protection strategies. Lastly, IBM Watson uses AI-driven privacy solutions to analyze and manage data risks efficiently. By integrating these additional tools into their operations, organizations can reinforce their ethical data trust endeavors.
- Privitar: Data Privacy Platform
The foundation of an effective data privacy platform lies in its ability to provide tools that ensure ethical data trust while maintaining user privacy. A well-designed platform allows organizations to easily access, analyze, and secure sensitive information without requiring extensive technical expertise. This democratization of data enables every team member to contribute to privacy-centric strategies, fostering an environment that prioritizes ethical considerations.
To achieve ethical data trust, the platform typically operates through key functionalities. First, it provides a centralized library where organizations can store and analyze user interactions, thereby revealing pain points as well as user desires. Next, it incorporates sophisticated algorithms to extract valuable insights from customer data, allowing teams to focus on enhancing the user experience. By viewing actionable reports, organizations can continuously adapt their practices, ensuring they respect user privacy while maximizing the value of their data.
- OneTrust: Privacy, Security & Data Governance Tool
Organizations today prioritize the management of privacy and security data to build trust with their stakeholders. A robust tool can play a pivotal role in this journey toward establishing Ethical Data Trust. By providing functionalities that streamline privacy governance, data security, and compliance management, a well-designed platform empowers organizations to uphold ethical standards in data practices.
The effectiveness of an organization’s data strategies hinges on several components. First, it aids in dissecting regulatory requirements and ensuring compliance. Secondly, it aids organizations in maintaining transparency, allowing users to understand how their data is utilized. Finally, by embedding security protocols, it assures clients that their sensitive information remains protected. By strategically implementing such a tool, organizations can foster a reliable environment while reinforcing their commitment to ethical data practices.
- BigID: Data Intelligence Platform
The Data Intelligence Platform serves as a crucial component in fostering Ethical Data Trust within organizations. Its user-friendly environment empowers individuals across all levels to access and utilize data effectively without requiring advanced technical expertise. By democratizing data insights, the platform ensures that every team member can engage with customer feedback and operational data, thereby enhancing the overall understanding of user privacy needs.
This platform features essential capabilities that facilitate the extraction of valuable insights from data. For example, it analyzes customer interactions, revealing pain points and desires expressed through various channels. Such transparency supports organizations in aligning their practices with ethical standards and building trust with their customers. Ultimately, by integrating these advanced tools into their operations, organizations can make informed decisions that prioritize user privacy and foster an ethical data ecosystem.
- IBM Watson: AI-Powered Privacy Solutions
Integrating AI into privacy solutions opens new avenues for fostering Ethical Data Trust. By utilizing advanced analytics, organizations can enhance data management practices. These AI-powered systems offer robust security measures while ensuring user privacy is prioritized. Transparency in data usage, informed user consent, and proactive measures to protect sensitive information are fundamental components of these solutions.
Furthermore, AI-driven privacy frameworks allow real-time monitoring and risk assessment, ensuring compliance with industry standards. Organizations adopting these technologies can adapt swiftly to evolving privacy regulations while building trust with their customers. The commitment to ethical practices creates an environment where users feel secure in sharing their data, ultimately contributing to stronger relationships and better business outcomes. With these innovative tools, fostering an ethical, privacy-centric approach is not just achievable, but essential for long-term success.
Conclusion on Building Ethical Data Trust Strategies
Establishing an Ethical Data Trust is essential for fostering long-term relationships with stakeholders. The foundation of this trust lies in transparency, user-centric practices, and continuous improvement. Organizations must be proactive in communicating how they collect, manage, and use data, ensuring individuals feel secure and respected. Ethical Data Trust not only enhances user confidence but also promotes loyalty and engagement in a competitive landscape.
Furthermore, integrating regular assessments and privacy by design principles into operations can drive accountability. By prioritizing ethical standards, organizations will not only comply with regulations but also create a culture of respect toward data privacy. Ultimately, building Ethical Data Trust strategies is not merely a compliance exercise; it is a pathway to building resilient connections in the digital age.
Analyze & Evaluate Calls. At Scale.