Qualitative data analysis offers a rich landscape of methods often overlooked in conventional discussions. Amidst the hustle of quantitative metrics, underrated qualitative methods can reveal profound insights that numbers alone cannot capture. They help researchers and practitioners understand the human experience behind the data, providing context and depth that enhances decision-making processes.
As we explore these underrated methods, we encourage you to look beyond traditional techniques. Embracing innovative qualitative approaches not only enriches analysis but also illuminates personal narratives and cultural nuances. By integrating these techniques, you can uncover new dimensions of understanding that significantly contribute to your organization's growth and innovation.
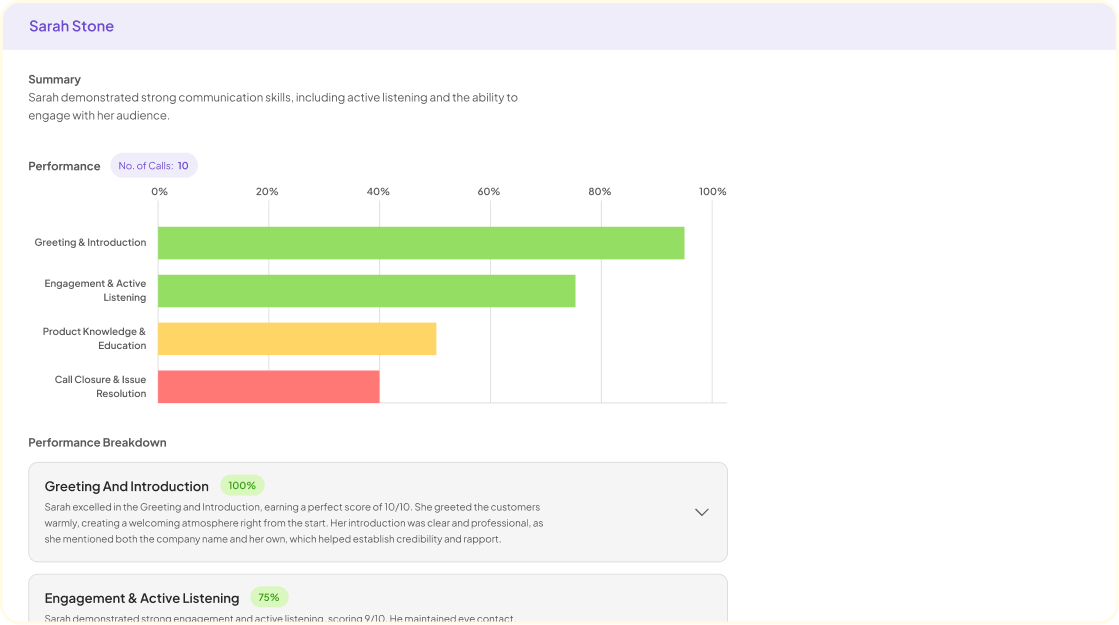
Analyze & Evaluate Calls. At Scale.

The Shift Towards Underrated Qualitative Methods
In recent years, qualitative research has seen a resurgence, yet many methods remain underappreciated. Factors like personal biases and a reliance on quantitative data can overshadow these underrated qualitative methods. Using narrative analysis, for example, researchers can uncover personal stories that reveal hidden truths within data frameworks.
Ethnographic study serves as another valuable tool, providing researchers with an immersive experience. By observing and recording cultural interactions, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of user behaviors and motivations. This approach can challenge preconceived notions about target audiences, leading to richer insights. Together, these underrated qualitative methods can illuminate aspects of human experience often neglected in more mainstream analyses. Embracing them opens doors to creating more meaningful connections with diverse populations.
The Landscape of Underrated Qualitative Methods
Qualitative methods often receive less attention compared to their quantitative counterparts, yet they hold immense potential for in-depth understanding. Exploring underrated qualitative methods reveals fascinating approaches to data analysis that remain underutilized. These methods embrace the complexity of human experiences, allowing researchers to gain insights that traditional techniques may overlook.
One promising approach is narrative analysis, which focuses on identifying stories within data to uncover underlying themes. It allows researchers to explore individual perspectives and experiences in a rich context. Ethnographic study, another underrated qualitative method, employs immersive observation techniques to document interactions. By engaging deeply with subjects, researchers can interpret cultural nuances that reveal how people relate to their environments.
These qualitative methods can transform data into meaningful narratives, offering nuanced insights into human behavior and decision-making. By embracing these underrated techniques, researchers can elevate their qualitative data analysis and ultimately inform more effective strategies.
Historical Context of Qualitative Analysis
Qualitative analysis has evolved significantly over time, often influenced by various academic and practical needs. Historically, qualitative methods were initially sidelined in favor of quantitative techniques, which dominated research landscapes due to their perceived objectivity. However, this shift began changing as researchers recognized the value embedded in narratives and human experiences. This gradual acceptance laid the groundwork for what we now understand as underrated qualitative methods in contemporary analysis.
The journey of qualitative analysis has seen the emergence of various techniques that remain relatively underappreciated today. Approaches like narrative analysis and ethnographic studies offer profound insights into human behavior, yet are often overlooked in favor of more mainstream methodologies. By revisiting these methods and understanding their historical context, researchers can uncover rich, nuanced data that may vastly improve their findings and interpretations. As we explore these underrated qualitative methods, acknowledging their past significance will be crucial in valuing their contribution to data analysis today.
The Shift Towards Underrated Qualitative Methods
As organizations face an ever-increasing volume of qualitative data, many are exploring underrated qualitative methods to enhance their analysis. Traditional techniques often fall short in capturing the nuances present in qualitative feedback, leading to a growing recognition of alternative approaches. These underrated qualitative methods not only provide deeper insights but also enable companies to act swiftly on customer signals, ensuring they stay ahead in competitive markets.
The shift towards these methods reflects the desire for more meaningful and timely analysis. Companies are now seeking innovative ways to engage with customer experiences, emphasizing the importance of understanding context and subtext within data. Techniques like narrative analysis and ethnographic studies allow businesses to explore the rich stories behind customer interactions, paving the way for actionable insights. Embracing these underrated approaches can transform qualitative data analysis from a cumbersome task into a dynamic resource for informed decision-making.
Extract insights from interviews, calls, surveys and reviews for insights in minutes
Delving into Specific Underrated Qualitative Methods
In the quest to harness the full potential of qualitative data, many research practitioners overlook underrated qualitative methods. These techniques provide nuanced insights and often reveal deeper layers of understanding within the data. By exploring specific underrated methods, researchers can enrich their analyses and develop a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Narrative analysis is a prominent example of an underrated qualitative method. This approach focuses on identifying and interpreting stories within the data, helping researchers understand how individuals construct meaning through their experiences. Another valuable technique is ethnographic study, which involves immersive observation to capture cultural interactions. Using these methods can uncover previously hidden dimensions of research questions, enhancing both data richness and depth. Embracing these underrated qualitative methods can significantly elevate the quality and impact of qualitative research findings.
Method 1: Narrative Analysis
Narrative analysis stands out as a fascinating yet underrated qualitative method offering deep insights into data. This technique involves unearthing stories present within qualitative data, helping researchers understand the human experiences that shape patterns and trends. By focusing on the narrative structure of each story, analysts can explore themes and emotions that traditional analysis methods might overlook.
To effectively conduct narrative analysis, one must follow two key steps. First, identifying stories within the data entails sifting through responses or transcripts to find personal accounts or anecdotes. Second, analyzing the structure and content involves dissecting these narratives to understand their context, significance, and underlying messages. This approach not only enriches the analysis but also reveals essential insights that can guide decision-making. Engaging with narrative analysis can breathe life into qualitative research, making it an invaluable tool for understanding complex human experiences.
Step 1: Identifying Stories within Data
Identifying stories within data is crucial for effective qualitative analysis. This step allows us to uncover the rich narratives woven into the fabric of collected information. Data is often seen as a series of numbers or responses, yet beneath this surface lies a wealth of insights and personal experiences waiting to be revealed.
To effectively identify these stories, begin by categorizing your data into manageable themes. This can include pain points, trends, or recurring phrases mentioned by participants. As you sift through the data, note the emotional undertones and motivations driving the responses. This approach not only highlights the human element but also enriches your overall analysis. Ultimately, identifying stories within data is among the most underrated qualitative methods, emphasizing the importance of context and nuance in understanding complex information. By prioritizing narrative over mere data points, we can transform our findings into compelling stories that resonate with stakeholders.
Step 2: Analyzing Structure and Content
In analyzing structure and content, it is essential to systematically approach the qualitative data collected. Consider beginning with identifying recurring themes or patterns that emerge from your data. This step allows you to pinpoint crucial elements that might otherwise be overlooked. Once themes have been identified, examine how they interconnect and contribute to the overall narrative. Understanding these connections is vital for drawing meaningful insights from your analysis.
Moreover, take the time to assess the language used within the data. The choice of words can unveil underlying sentiments and attitudes, revealing deeper truths about the subjects involved. Utilizing underrated qualitative methods, such as narrative analysis, enables you to appreciate these nuances. Through such scrutiny, you can craft a comprehensive understanding of your qualitative findings and present them effectively to your audience. Embracing these often-overlooked approaches can significantly enhance the value derived from qualitative analysis.
Method 2: Ethnographic Study
Ethnographic studies offer a profound lens through which researchers can observe behaviors in their natural context. This underrated qualitative method emphasizes immersion, providing an opportunity to gather genuine insights that surveys or interviews might overlook. Researchers engage directly with participants, observing practices, rituals, and interactions that define their cultural environment.
The process involves two main steps. First, immersive observation techniques allow researchers to immerse themselves fully in the participant’s environment, providing rich, contextual data. Second, recording and interpreting cultural interactions reveals the nuances behind participant behavior, preferences, and motivations. By adopting this method, researchers can unlock layers of meaning that may go unnoticed through traditional data collection methods. Ultimately, an ethnographic study can illuminate intricate dynamics, thereby enhancing qualitative analysis and fostering a deeper understanding of human experiences.
Step 1: Immersive Observation Techniques
Immersive observation techniques offer a unique approach to qualitative data analysis, immersing researchers in the environments they study. This method encourages an in-depth understanding of participants' interactions and behaviors, uncovering insights that traditional methods may overlook. By observing with intent, researchers can identify patterns and nuances that inform the underlying dynamics of a situation.
During this step, researchers engage closely with their subjects, taking notes on their surroundings and interactions. This process is essential for capturing the rich context in which behaviors occur. By combining observational data with participant feedback, researchers can construct a multifaceted view of the phenomena at hand. Employing these underrated qualitative methods allows for a deeper exploration into the complexities of human behavior, providing invaluable insights that drive better decision-making and foster innovation.
Step 2: Recording and Interpreting Cultural Interactions
Understanding cultural interactions is essential in qualitative research, as these encounters reflect deeper societal values and beliefs. Step 2 involves both recording and interpreting these interactions. First, capturing cultural nuances requires attentive observation and detailed documentation. This might include transcribing conversations, recording interviews, or taking field notes, which serve as the raw materials for analysis.
Next comes interpretation, where the goal is to uncover underlying meanings in the recorded data. This process allows researchers to identify patterns, themes, and contextual elements critical to understanding participants' perspectives. By embracing underrated qualitative methods, researchers can enhance their analyses, leading to richer insights and a deeper appreciation of cultural dynamics. Exploring these interactions can ultimately help inform strategies in various fields, from marketing to social science, providing a comprehensive viewpoint on the subjects at hand.
Tools and Resources for Employing Underrated Qualitative Methods
Employing underrated qualitative methods requires the right tools and resources to ensure effective data analysis. One of the most notable tools in this domain is NVivo. This software allows researchers to organize data, develop codes, and visualize complex narratives. Similarly, MAXQDA provides robust features for analyzing textual and multimedia information, making it easier to identify themes across various datasets.
Additionally, Dedoose stands out for its user-friendly interface and capabilities in mixed-methods research. It facilitates collaboration among team members, which is essential when exploring diverse qualitative insights. Lastly, ATLAS.ti offers powerful coding features that help researchers delve into the relationships between qualitative variables. By utilizing these tools, researchers can unlock the power of underrated qualitative methods to generate deeper, more meaningful insights in their analyses. Utilizing the right resources not only enhances the quality of findings but also broadens the understanding of qualitative data analysis techniques.
Insight7: Leading the Charge in Qualitative Tools
In the realm of qualitative research, innovative tools can transform how organizations understand customer insights. "Insight7: Leading the Charge in Qualitative Tools" emphasizes the necessity for advanced methodologies in qualitative data analysis. Today's businesses are inundated with customer signals, yet traditional analysis methods often fail to keep pace. The demand for effective, timely insights calls for a fresh approach that integrates underrated qualitative methods into standard practice.
Successful qualitative analysis is not merely about collecting data; it's about discerning themes and connections that influence strategy and decision-making. By employing tools that prioritize efficiency and collaboration, organizations can better streamline processes and fully exploit their qualitative data. This includes utilizing platforms that facilitate narrative and ethnographic studies, allowing researchers to identify deeper meanings and cultural nuances in customer feedback. Ultimately, adopting these underrated qualitative methods opens new avenues for innovation and competitiveness in today’s market.
Other Useful Tools
In the realm of qualitative research, various underrated qualitative methods can benefit significantly from specialized tools. NVivo, for instance, offers powerful capabilities for coding and analyzing unstructured data, making it a go-to option for researchers. Its robust features allow users to effortlessly organize and visualize patterns within complex datasets. Additionally, MAXQDA provides versatile tools for qualitative analysis, emphasizing user-friendliness while maintaining in-depth functionality.
Dedoose is another tool that deserves recognition for its collaborative features. It allows teams to analyze qualitative and quantitative data in tandem, simplifying the research process. ATLAS.ti rounds out this toolset by providing a dynamic environment for in-depth data visualization and analytical rigor. Each of these tools serves as a platform for applying underrated qualitative methods effectively, enabling researchers to glean more nuanced insights from the data they gather. Investing time in exploring these tools can elevate qualitative analysis to new heights.
- NVivo
NVivo serves as a powerful tool in qualitative data analysis, offering researchers an efficient platform to manage and interrogate their datasets. This software shines in organizing various forms of data, such as audio transcripts, images, or survey responses, making it incredibly versatile. Users can effortlessly create projects where they can compile a range of materials, which allows for more nuanced analysis. The ability to visualize historical queries and extract testimonials quickly enhances its usability, especially for marketing teams seeking positive feedback.
Navigating the features of NVivo reveals a range of underrated qualitative methods that can enrich your analysis. For example, the matrix function provides a straightforward way to compare data points across multiple sources. Questions posed during analysis can yield insightful patterns and trends, answering specific inquiries about customer sentiments or product evaluations. By embracing NVivo, researchers can exploit these overlooked qualitative techniques that enhance understanding and, ultimately, decision-making.
- MAXQDA
MAXQDA stands out as a powerful tool in the realm of qualitative data analysis. Its design allows researchers to easily upload various types of data, including transcripts and audio files. This simplicity in data management enables users to create projects swiftly and focus on deeper analysis rather than getting bogged down in logistics. By integrating multiple data sources seamlessly, users can visualize key insights that often go unnoticed, enhancing the overall analytical experience.
What makes MAXQDA particularly attractive is its ability to identify trends and patterns within qualitative data efficiently. Researchers can formulate specific questions about customer feedback or themes emerging from interviews. As they explore these queries, the application’s framework allows for straightforward comparisons and summations, revealing the nuanced narratives hidden in the data. By harnessing MAXQDA, analysts can effectively leverage underrated qualitative methods, thus transforming raw insights into actionable decisions.
- Dedoose
In the realm of qualitative data analysis, certain tools remain underappreciated despite their potential to revolutionize research outcomes. Dedoose, a cloud-based platform, streamlines the qualitative coding process and enhances collaboration among researchers. Its user-friendly interface allows teams to analyze mixed-methods data efficiently, making it a valuable asset in uncovering nuanced insights. By facilitating the integration of qualitative and quantitative data, it supports a comprehensive understanding of research themes.
Moreover, the tool's capabilities for visualizing data trends can lead to innovative interpretations that often get overlooked. As researchers explore the dimensions of qualitative data, the use of underrated qualitative methods becomes essential. Utilizing Dedoose can illuminate findings that might otherwise remain hidden, enabling scholars and practitioners to make data-driven decisions that are meaningful and impactful. Embracing this tool not only optimizes analysis but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the complexities of human experiences captured in qualitative research.
- ATLAS.ti
ATLAS.ti serves as a powerful tool for qualitative data analysis, offering features that can elevate your research process. By introducing a project-based approach, researchers can effectively organize and analyze their qualitative data. This method allows users to easily upload diverse file types, including transcripts and audio recordings, into one cohesive workspace.
One of the standout features is its ability to summarize data trends and patterns efficiently, making it indispensable for identifying insights quickly. With customizable projects, users are empowered to explore and interrogate their data in a systematic manner. Whether examining customer feedback or distilling complex interviews, the tool's intuitive interface supports the exploration of underrated qualitative methods that often go unnoticed. Integrating such tools into qualitative analysis can unlock new perspectives and enhance understanding in various research contexts.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Underrated Qualitative Methods
In conclusion, embracing underrated qualitative methods can significantly enhance our understanding of complex data. These techniques, often overlooked, offer unique insights that traditional methods may miss. By integrating narrative analysis and ethnographic studies into our approach, we unveil richer stories and cultural contexts that inform our decisions.
Recognizing the value of these methods empowers us to tap into diverse perspectives. Ultimately, this shift towards embracing underrated qualitative methods not only refines our analysis but also paves the way for innovative solutions in our work, enriching the overall research landscape.