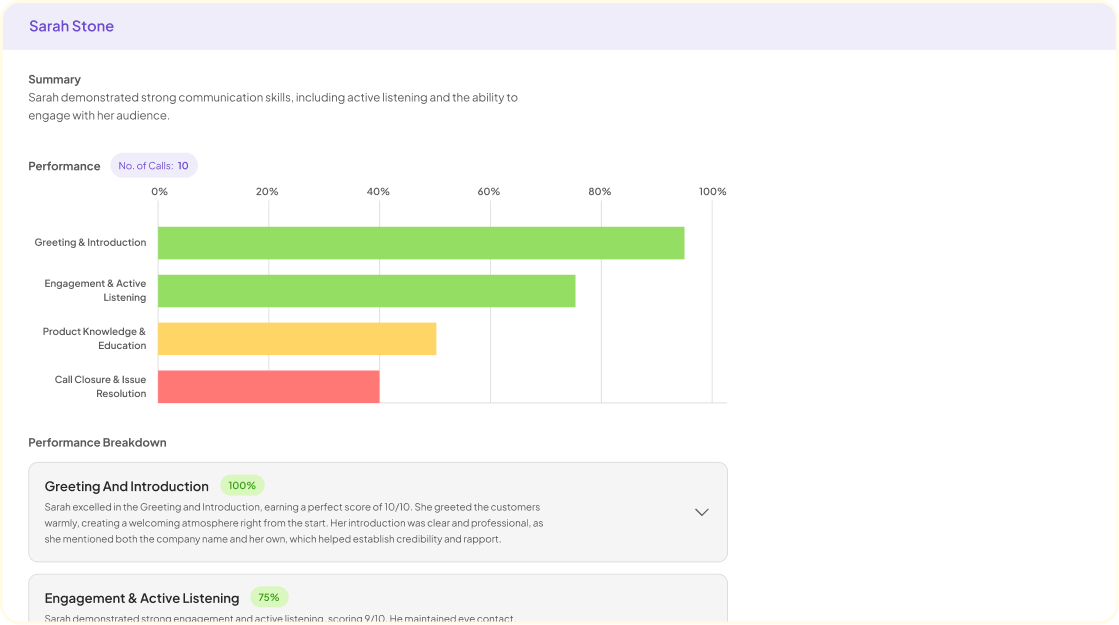
Qualitative data management is essential for transforming raw data into meaningful insights in research projects. As researchers collect interviews, focus groups, and other narrative forms, the challenge lies in organizing and interpreting this information. Without effective management, valuable insights can easily be lost, leading to incomplete analyses and misguided conclusions.
In this introductory section, we will explore the fundamental principles of qualitative data management. By implementing structured methodologies, researchers can identify patterns and trends, which are crucial for fulfilling research objectives. Establishing clear workflows and data categorization empowers researchers to navigate complex information more efficiently, ultimately enhancing the quality and reliability of their findings. Understanding these management strategies is vital for anyone looking to excel in qualitative research.
Importance of Qualitative Data Management
Qualitative Data Management is essential for effectively harnessing the insights gathered from interviews and focus groups. The significance of managing qualitative data lies in its ability to transform rich, narrative information into actionable intelligence. When qualitative data is well-organized, researchers can easily retrieve and analyze it to inform strategic decisions. This seamless access enables teams to respond swiftly to market demands and customer needs, ultimately fostering a competitive edge.
Moreover, qualitative data management ensures that insights are not lost in fragmentation. By centralizing data storage, teams can collaborate more efficiently and maintain a clear narrative across their findings. This enhanced communication empowers researchers to generate more cohesive reports that resonate with stakeholders. As insights from qualitative data become increasingly vital in research projects, the importance of their management cannot be overstated. Effective Qualitative Data Management directly contributes to enhanced research outcomes, making it a cornerstone for successful research endeavors.
Key Challenges in Managing Qualitative Data
Managing qualitative data presents several key challenges that can complicate the research process. First and foremost, the sheer volume of data collected during interviews and focus groups can be overwhelming. Researchers often find it difficult to sift through and accurately analyze this rich but unstructured information. Compounding this issue is the need for meticulous coding and categorization, which is labor-intensive and requires a deep understanding of the content.
Another significant challenge lies in ensuring consistency and reliability in data interpretation. Multiple analysts examining the same qualitative data can yield varying interpretations, leading to discrepancies in findings. This inconsistency can affect the overall insights derived from the research, making stakeholder buy-in more challenging. Additionally, efficient collaboration among team members can be stunted when insights are stored in different formats and locations, resulting in a scattered approach to analysis. Addressing these challenges is essential for effective qualitative data management, enabling researchers to turn insights into actionable strategies.
Strategies for Effective Qualitative Data Management
Establishing effective qualitative data management starts with creating a structured framework for how data will be collected, organized, and analyzed. Begin by defining clear objectives for your research, as this provides direction. Implement standardized criteria for data collection, ensuring consistency across various sources. Utilizing transcription tools can facilitate the conversion of interviews and calls into structured data. This ensures that your team can easily reference and analyze the qualitative data collected.
Additionally, developing a robust coding system is essential for analyzing qualitative data efficiently. By categorizing responses based on common themes, you can distill large amounts of information into actionable insights. Regularly revisiting and updating these codes can enhance data accuracy over time. Finally, ensure that you store and back up all qualitative data securely, preventing any loss and maintaining participant confidentiality. This organized approach to qualitative data management will enhance the reliability and validity of your research findings.
Tools and Techniques for Qualitative Data Management
Managing qualitative data effectively is crucial for drawing meaningful insights from research projects. Various tools and techniques assist researchers in achieving this goal. First, transcription software simplifies the process of converting recorded interviews into text. This allows for smoother data analysis. Next, qualitative analysis software, such as NVivo or Atlas.ti, offers functionalities for coding and organizing themes within datasets. These platforms can reveal patterns over time, making it easier to understand participants' perspectives.
Additionally, creating matrices or spreadsheets helps researchers consolidate and compare specific data points across multiple interviews. This visual representation makes identifying trends straightforward. Participatory analysis methods, involving stakeholders in the review process, can also enhance the depth of qualitative insights. By employing these tools and techniques, researchers can ensure effective qualitative data management, ultimately leading to richer and more actionable findings in their projects.
Selecting the Right Tools for Data Collection
Selecting the right tools for data collection is crucial in managing qualitative data effectively. The tools chosen should align with your research objectives and the nature of your qualitative data. This ensures that the information gathered is relevant and can be analyzed efficiently.
When selecting your tools, consider several key factors. First, evaluate the features offered by different tools, such as transcription capabilities, data storage, and analysis functionalities. Second, assess ease of use; tools should not complicate the data collection process. Third, consider integration with existing software, as seamless connectivity can enhance your qualitative data management efforts. Lastly, budget constraints play an essential role; prioritize cost-effective tools that do not compromise on quality. By thoughtfully selecting the right tools, researchers can streamline their data collection processes and focus on deriving meaningful insights from their qualitative data.
Techniques for Data Organization and Analysis
Managing qualitative data effectively is crucial for uncovering insights in research projects. A strong technique for data organization includes creating thematic categories based on the key themes that emerge from your data. This involves reviewing transcripts to identify patterns, coding responses for easier retrieval, and summarizing findings concisely.
Next, employing analytical frameworks such as matrices can enhance qualitative data management. For instance, you can use a matrix to examine specific questions across multiple interviews, highlighting recurring pain points and concerns. This structured approach provides clarity and allows researchers to visualize the interplay of various themes, making it easier to draw actionable conclusions. Data organization is not just about storage; it's about making qualitative data accessible for thorough analysis and informed decision-making. Systems for coding and thematic analysis are essential for transforming raw data into meaningful insights.
Conclusion on Qualitative Data Management in Research Projects
Effective qualitative data management is essential for enhancing the reliability and relevance of research findings. A structured approach to managing qualitative data not only ensures meaningful insights but also allows for a more nuanced analysis of participant perspectives. By organizing and interpreting data systematically, researchers can reveal underlying patterns that inform decision-making processes.
In conclusion, prioritizing qualitative data management within research projects facilitates the extraction of valuable insights. Researchers can develop a comprehensive understanding of complex topics, ensuring that their findings resonate with stakeholders. Ultimately, effective management enhances the rigor of research and contributes to informed strategies that address real-world challenges.