Customer Journey Map vs. Process Map: Key Differences
-
Bella Williams
- 10 min read
Mapping Perspective Differences play a crucial role in understanding how customer journey maps and process maps serve distinct purposes. Both maps can provide valuable insights, but they must be viewed from different angles, focusing on the customer versus the internal processes of a business.
To truly grasp these differences, it’s essential to adopt a multifaceted viewpoint. A customer journey map centers on customer experiences and emotions, while a process map illustrates workflow efficiencies and roles within an organization. By comprehending these distinctions, businesses can develop strategies that not only align with customer expectations but also enhance operational performance.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.
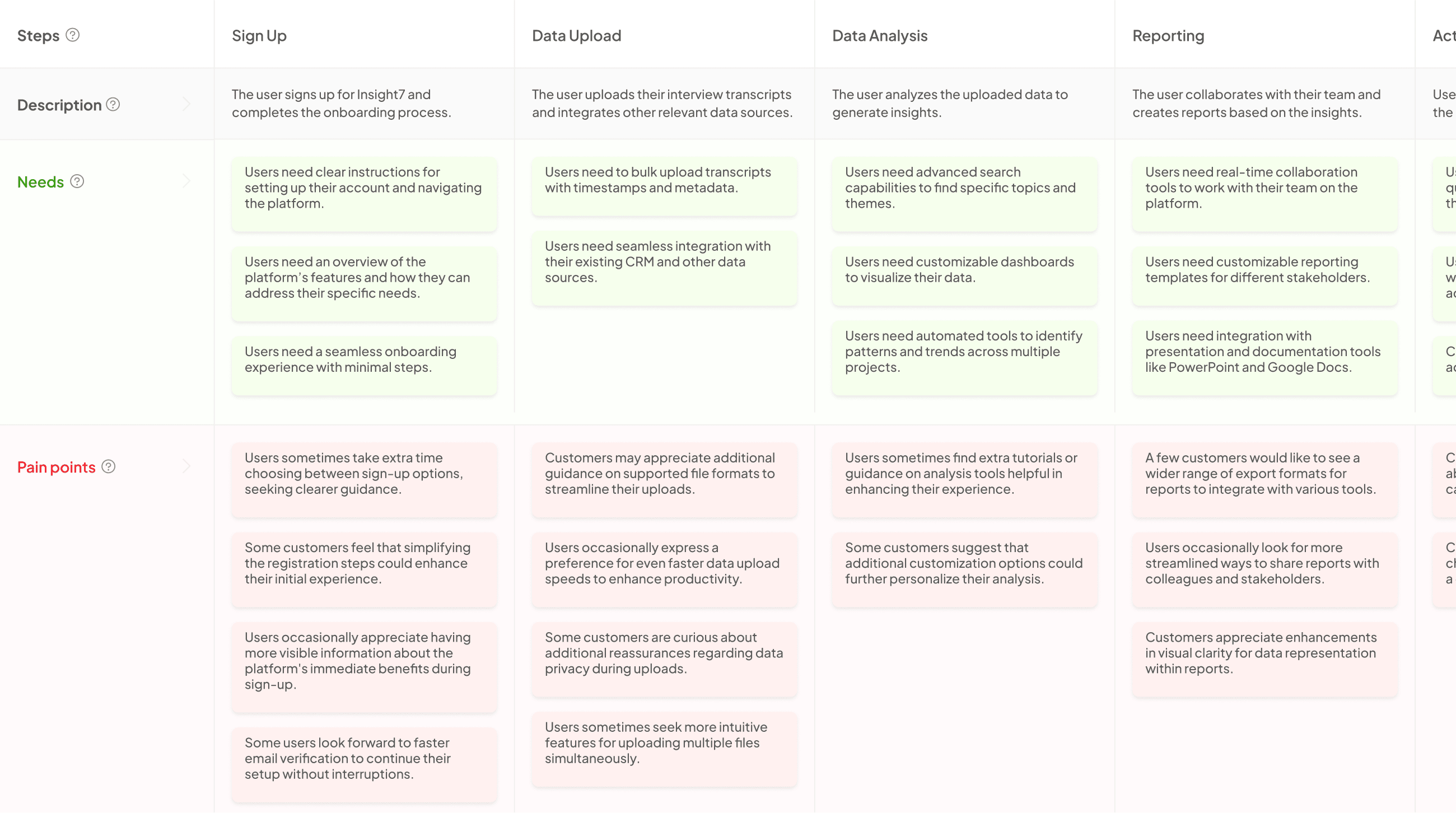
Customer Journey Map: Mapping Perspective Differences on Human Experience
Mapping perspective differences on human experience is essential to developing a relatable and impactful customer journey map. By understanding each unique interaction a customer has with a brand, businesses can better tailor their strategies to meet emotional and practical needs. This approach brings to light the various touchpoints through which customers engage, ultimately helping to create a more human-centric experience.
Furthermore, integrating qualitative research into this mapping process enriches the understanding of customer behavior. It enables businesses to tap into insights that capture the customer’s emotions and motivations throughout their journey. These insights can guide improvements and innovations that resonate deeply with customers, ensuring a more meaningful connection. Thus, successful customer journey mapping is rooted in recognizing diverse perspectives and experiences that shape how customers interact with businesses.
Emotional Engagement and Behavior Tracking
Understanding emotional engagement and behavior tracking is essential when differentiating between a customer journey map and a process map. Emotional engagement refers to the feelings customers encounter at various points in their journey. By recognizing these emotions, businesses can tailor their strategies to address customer needs more effectively. Mapping perspective differences highlight how a customer-centric approach helps in identifying phases like awareness and consideration, where emotions such as curiosity and concern come into play.
Behavior tracking complements this by offering insights into how customers react in response to these emotions. This combination allows businesses to adapt messaging and experiences to align with customer sentiment. For instance, showcasing product attractiveness during the initial awareness phase can engage curious potential buyers, whereas addressing functionality and cost in the consideration phase can alleviate concerns. Collecting objective data through surveys and interviews is crucial to this understanding, ensuring strategies resonate with genuine customer experiences.
Stages of the Customers Journey
Understanding the stages of the customer journey is crucial in creating effective marketing strategies. Each stage represents a unique phase where customers evaluate their needs and experiences with a brand. The journey typically consists of several stages, including awareness, consideration, decision, and retention. In the awareness stage, potential customers discover a brand or product, while in the consideration stage, they actively explore options that meet their needs.
In the decision stage, customers choose a product and make a purchase. Finally, the retention stage focuses on keeping customers engaged, fostering loyalty, and encouraging repeat business. By mapping these stages, businesses can tailor their communication strategies and optimize customer interactions. Mapping perspective differences highlight how different visuals can showcase the customer experience more effectively. In this way, companies can ensure they align their operations with customer expectations throughout each phase of their journey.
Generate Journey maps, Mind maps, Bar charts and more from your data in Minutes
Process Map: Mapping Perspective Differences on Operational Efficiency
Process maps and customer journey maps differ significantly in their focus on operational efficiency. When examining mapping perspective differences, it’s essential to recognize that process maps outline the steps involved in operational workflows. They provide a detailed visual representation of tasks, responsibilities, and sequences, emphasizing how processes are executed within an organization.
Conversely, customer journey maps prioritize the customer’s experience, illustrating their interactions with a product or service. These maps highlight emotional touchpoints and friction experienced during a customer’s path. Understanding these mapping perspective differences helps organizations to optimize their internal operations while enhancing the overall customer experience. In doing so, businesses can achieve a balance between efficiency and satisfaction, ultimately driving improved performance and loyalty.
Workflow and Efficiency Optimization
Understanding the mapping perspective differences between customer journey maps and process maps is crucial for optimizing workflows and efficiency. A well-defined workflow can streamline operations by clarifying roles and tasks, which ultimately enhances productivity. When businesses clearly distinguish between these mapping techniques, they can better tailor their processes to fit specific goals, ensuring a smoother execution of tasks.
To achieve effective workflow and efficiency optimization, consider the following key factors:
- Clarity of Purpose: Clearly define what you aim to achieve with either map. Customer journey maps focus on user experience, while process maps address internal efficiency.
- Integration of Insights: Utilize findings from both maps to inform decisions. Combining perspectives can reveal gaps in the workflow and highlight inefficiencies.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly revisit and update both maps. Adapt existing workflows as customer needs or internal processes evolve, ensuring sustained efficiency.
By applying these principles, organizations can significantly enhance their overall performance, achieving a more refined workflow that meets both customer and operational demands.
Identifying Process Bottlenecks
Identifying process bottlenecks is essential for optimizing organizational efficiency. By thoroughly examining both customer journey maps and process maps, you can pinpoint critical friction points that hinder performance. Often, these bottlenecks emerge from redundant steps, lack of resources, or miscommunication among team members.
To effectively identify process bottlenecks, consider these steps:
- Map the Entire Process: Visualize every step your customers take and every action your team performs. This will illuminate where delays occur.
- Gather Feedback: Engage with both customers and employees to collect insights on pain points. Their perspectives often reveal hidden obstacles.
- Analyze Data: Utilize metrics and analytics to track process performance and identify discrepancies between expected outcomes and actual results.
- Prioritize Issues: Not all bottlenecks are created equal. Focus first on those that most significantly impact customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
By addressing these bottlenecks systematically, you enhance the overall flow of your processes, leading to a more seamless experience for customers and staff alike.
Conclusion: Bridging the Mapping Perspective Differences
Bridging the mapping perspective differences between customer journey maps and process maps offers valuable insights for businesses. By understanding these distinct tools, organizations can better address customer needs and operational efficiency. Customer journey maps focus on the user experience, capturing emotions and touchpoints that guide potential and existing customers. In contrast, process maps emphasize sequential tasks and workflows necessary to deliver a product or service effectively.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.

Recognizing these differences allows businesses to create a comprehensive view of both customer interactions and internal processes. By integrating both mapping perspectives, organizations can enhance their strategies, ensuring that customer experiences align with operational capabilities. This holistic understanding ultimately leads to improved satisfaction and sustainable growth.







