6 Process Mapping Methodologies Compared and Explained
-
Bella Williams
- 10 min read
Process mapping serves as a fundamental tool for organizations looking to optimize their workflows. By visually representing processes, teams can identify bottlenecks, enhance efficiency, and improve outcomes. Navigating the diverse landscape of process mapping methodologies can be challenging, especially when seeking the best fit for specific organizational needs.
Understanding process mapping comparison is critical for determining which methodology aligns with your goals. This section will delve into six distinct process mapping methods, exploring their unique attributes and advantages. As we compare these methodologies, you’ll gain insights into how each approach can support your organization in achieving improved performance and enhanced user experiences.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.
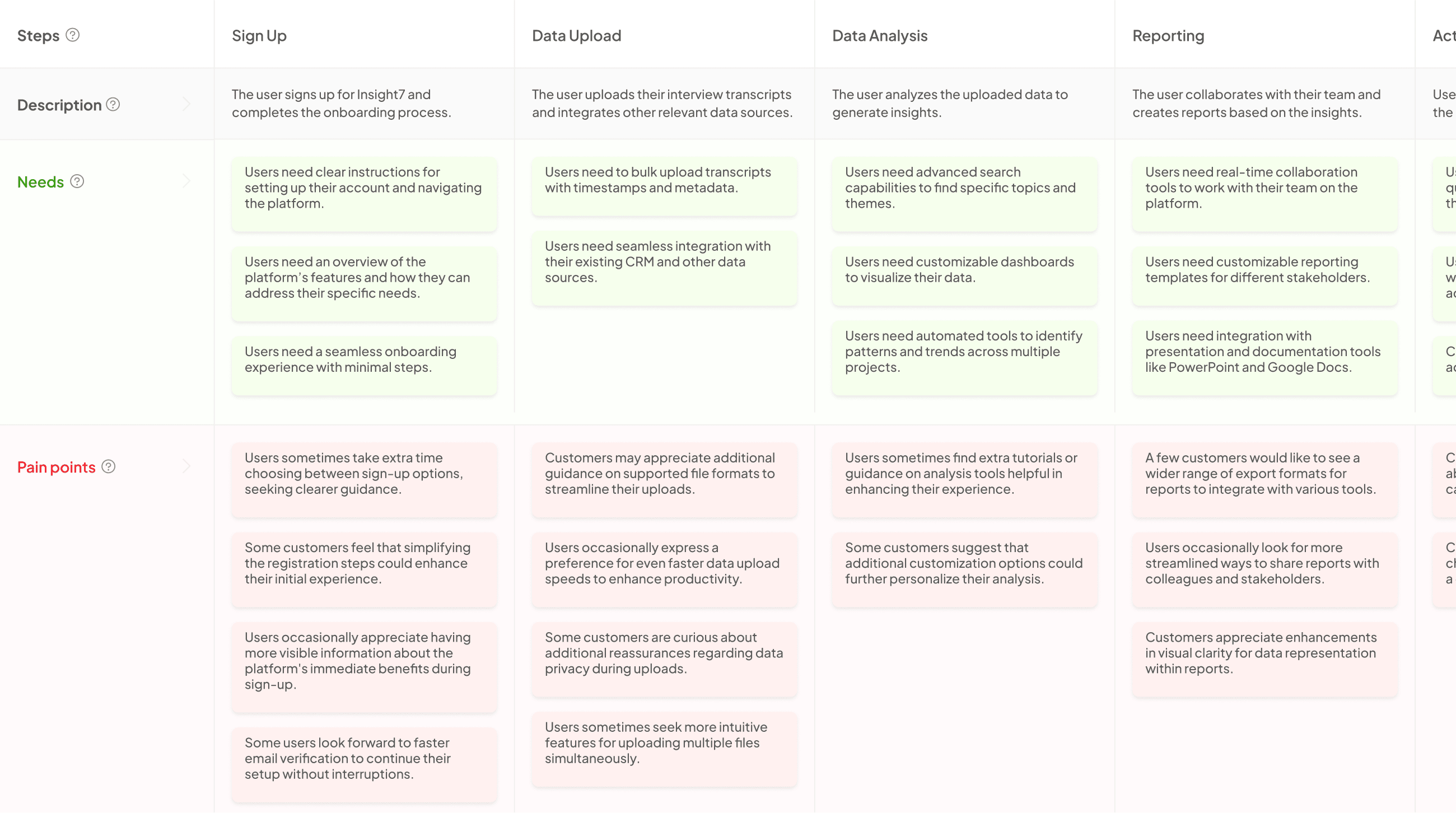
What is Process Mapping?
Process mapping serves as a valuable visual representation of the steps involved in a particular workflow. By outlining each step in a process, organizations can better understand how tasks are completed and identify areas for improvement. It allows teams to analyze complexity, streamline operations, and ensure that everyone involved has a clear understanding of their roles.
Effective process mapping contributes significantly to Process Mapping Comparison, as various methodologies can be applied in different contexts. Common techniques include flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and value stream mapping. Each method offers unique advantages, catering to specific needs such as process optimization or enhancing team collaboration. By comparing these methodologies, organizations can select the most suitable approach for their projects, ultimately leading to increased efficiency and better outcomes.
Importance of Process Mapping in Business
Process mapping plays a crucial role in enhancing business efficiency and understanding how processes flow within an organization. By visually detailing each step in a process, teams can identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. This clarity not only supports task delegation but also fosters accountability and ownership among team members. When businesses engage in a thorough process mapping comparison, they discover various methodologies that suit specific operational needs.
Moreover, process mapping helps in aligning teams towards common goals by establishing a shared understanding of workflows. It encourages cross-departmental collaboration, allowing for a seamless exchange of insights and expertise. By prioritizing process mapping, companies can make informed decisions grounded in a clear understanding of their operations, ultimately leading to enhanced productivity and performance. Establishing a structured approach through these comparisons serves as a foundation for consistent improvement across all sectors of the business.
Six Key Methodologies in Process Mapping Comparison
When exploring the “Six Key Methodologies in Process Mapping Comparison,” understanding each process mapping methodology is crucial. These methodologies provide different perspectives on visualizing and analyzing workflows, allowing organizations to enhance efficiency and clarity. Each approach offers unique tools, techniques, and advantages tailored to various needs and contexts.
The first methodology is flowcharting, which uses symbols to depict steps in a process. Next is SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers), offering a high-level overview that identifies key components. Thirdly, value stream mapping visualizes the flow of materials and information, emphasizing waste reduction. Additionally, swimlane diagrams delineate responsibilities across different departments or individuals. The fifth methodology, process mapping software, leverages technology to create dynamic, interactive maps. Lastly, the use of process flow diagrams provides a structured representation of processes, ensuring all elements are clearly illustrated. Each of these methodologies contributes to effective process mapping comparison by serving distinct purposes tailored to organizational needs.
Flowcharts
Flowcharts serve as a pivotal tool in process mapping, offering a visual representation of workflows. Typically, they include various shapes representing processes, decisions, and flow directions, which streamline communication across teams. This clarity allows individuals to identify inefficiencies and duplicate efforts within their operations, contributing to continuous improvement. By using flowcharts, teams can better understand complex processes, making them ideal for comparing methodologies in process mapping.
When comparing process mapping methodologies, flowcharts stand out due to their simplicity and effectiveness. They are particularly useful for illustrating both high-level overviews and intricate details of a process. This adaptability enhances data sharing and prompts collaborative discussions among stakeholders, which is crucial for successful implementations. As organizations strive for efficiency, flowcharts prove essential in visualizing and optimizing their processes, which is a critical aspect of any process mapping comparison.
Basics of Flowcharts
Flowcharts serve as powerful visual representations of processes, enabling teams to outline key steps easily. They utilize standardized symbols to illustrate different actions, decisions, and flows within a given procedure. Understanding these basics is essential for effective process mapping comparison and evaluation. By employing flowcharts, organizations can pinpoint inefficiencies and identify areas for improvement.
When creating a flowchart, it’s crucial to follow a few fundamental steps. First, define the process’s start and endpoints clearly. Next, list all the necessary steps and decisions involved. Third, choose appropriate symbols to represent each stage, such as ovals for starting points, rectangles for actions, and diamonds for decisions. Lastly, connect the symbols with arrows to indicate the flow of the process. This structured approach not only enhances clarity but also aids in better understanding when comparing various mapping methodologies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flowcharts
Flowcharts serve as a valuable visual aid in process mapping comparison, allowing complex information to be simplified. One advantage is their ability to enhance understanding and communication among team members. By visually representing steps, flowcharts can clear confusion and improve collaboration. Additionally, they can be easily modified, making them adaptable to process changes. Simple symbols and clear layouts help everyone grasp the processes quickly, increasing overall efficiency.
However, there are also disadvantages to consider. Flowcharts can become overly complex if too much information is included, leading to confusion rather than clarity. Furthermore, they may not always be suitable for capturing intricate processes, particularly where detailed explanations are required. Relying solely on flowcharts might also result in overlooking critical elements that are best represented in other forms of documentation. Balancing these advantages and disadvantages is essential for effective process mapping.
Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams provide a clear visualization of processes by distinguishing responsibilities across different stakeholders involved. Each lane represents a specific participant or group, organizing tasks in a manner that enhances understanding of process flow. This clarity helps identify when hand-offs occur, ensuring accountability by showing who is responsible for each action step.
When considering process mapping comparison, swimlane diagrams stand out for their intuitive layout. They not only depict step-by-step procedures but also highlight interactions between various actors. This allows teams to pinpoint bottlenecks and areas for improvement effectively. By displaying process ownership, swimlane diagrams assist organizations in streamlining workflows and enhancing communication, ultimately leading to more efficient outcomes. Whether for project management or operational analysis, swimlane diagrams offer an essential tool for visualizing complex interactions within processes.
Basics of Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams are a powerful visual tool used in process mapping to clarify responsibilities and workflows. Each lane in the diagram represents a different role or department, allowing users to see how tasks flow across different segments and who is responsible for each task. This format effectively highlights dependencies and interactions between various roles, enhancing communication and accountability within teams.
Understanding the basics of swimlane diagrams can significantly aid in process mapping comparison. You can begin by identifying the actors involved in a process, which helps in creating distinct lanes for each. Next, map out the sequence of activities within these lanes, focusing on how the tasks interconnect between roles. Finally, this visualization aids in pinpointing bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement, ultimately facilitating better decision-making and process optimization. With these tools at your disposal, you’ll have a clearer perspective on how different process mapping methodologies can be utilized effectively.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams offer several advantages in process mapping. One key benefit is their ability to clearly distinguish responsibilities across different stakeholders or departments. This visual separation helps teams identify who is accountable for each step in a process, reducing confusion and increasing accountability. Additionally, swimlane diagrams simplify complex processes, making it easier for stakeholders to understand workflows at a glance, thus enhancing collaboration within teams.
However, there are also disadvantages to consider. Creating swimlane diagrams can be time-consuming, especially for intricate processes. They may become cluttered when representing many participants or complex tasks, which could overwhelm the audience. Furthermore, if not updated regularly, these diagrams can become outdated and lead to misinformation, counteracting their original purpose. Therefore, while swimlane diagrams are valuable tools, it’s essential to weigh both their strengths and limitations in any process mapping comparison.
Comparing Advanced Process Mapping Methodologies
Comparing advanced process mapping methodologies is essential for understanding how different techniques can enhance process analysis. Each methodology offers unique tools and frameworks that cater to specific organizational needs. Key factors for process mapping comparison include clarity, efficiency, adaptability, and stakeholder involvement.
Among the methodologies discussed, some utilize visual tools such as flowcharts, while others leverage data-driven approaches like journey mapping. These varying techniques can significantly impact the effectiveness of process improvement initiatives. It is crucial to evaluate the strengths and limitations of each methodology to determine which aligns best with your process optimization goals. Ultimately, a thoughtful comparison helps organizations make informed decisions, improve communication, and foster collaboration among stakeholders.
Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a powerful tool that provides clarity in process analysis and improvement. By visualizing the flow of materials and information through every step of a process, organizations can identify inefficiencies and areas for enhancement. This methodology emphasizes the value that each step adds, allowing teams to focus efforts on optimizing operations and reducing waste.
In the context of process mapping comparison, VSM stands out by not only documenting the current state but also illustrating a future state that aims for efficiency. It serves as a bridge between understanding existing workflows and implementing effective changes. When organizations adopt VSM, they can expect enhanced collaboration among departments as everyone aligns towards shared goals. Ultimately, employing Value Stream Mapping enables businesses to streamline processes and elevate customer satisfaction by delivering greater value at every stage.
Basics of VSM
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a vital tool in process mapping comparison. It visually represents the flow of materials and information through a process, enabling organizations to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. By showcasing both current states and future goals, VSM provides teams with a clear understanding of how processes function and where enhancements can be made.
Implementing VSM involves several key steps. First, the current state of the process is mapped, including all steps, delays, and resources. Next, teams analyze this map to pinpoint waste and inefficiencies. Lastly, a future state map is developed, illustrating the ideal process. This approach not only facilitates a better understanding of operations but also fosters collaboration among teams working toward the organization’s efficiency goals. Ultimately, grasping the basics of VSM enhances decision-making in the broader context of process mapping comparison.
Generate Journey maps, Mind maps, Bar charts and more from your data in Minutes
Advantages and Disadvantages of VSM
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) offers distinct advantages and disadvantages as a process mapping methodology. On the positive side, VSM allows organizations to visualize processes, identify inefficiencies, and enhance overall workflow. This method promotes teamwork by involving various stakeholders, leading to a more collaborative environment. Furthermore, its focus on value creation helps organizations streamline operations, ultimately boosting customer satisfaction.
Conversely, VSM does have its drawbacks. One limitation is that it can be time-consuming, particularly when mapping complex processes. Additionally, organizations may rely too heavily on this methodology, neglecting other valuable process mapping tools. This can lead to a narrow focus and potential oversight of broader organizational needs. In summary, while VSM has significant benefits in enhancing process efficiency, organizations must remain mindful of its limitations in a comprehensive process mapping comparison.
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN)
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) serves as a standardized method for visually representing business processes. It utilizes a flowchart-like structure to simplify the understanding of complex workflows. By incorporating various symbols and elements, BPMN allows stakeholders to communicate their processes efficiently. This clarity supports better decision-making and process optimization, vital in any successful organization.
When comparing process mapping methodologies, BPMN stands out for its versatility and ability to bridge the gap between technical and non-technical audiences. It enables organizations to document their operations comprehensively, facilitating improvements and alignment across departments. Additionally, BPMN supports different levels of detail, accommodating both high-level overviews and intricate process specifications. This adaptability makes it a valuable tool in the evolving landscape of process management, ranking it highly in process mapping comparison discussions.
Basics of BPMN
BPMN, or Business Process Model and Notation, is a standardized method for visualizing business processes. It uses a series of symbols and notations to create clear, understandable diagrams. This helps organizations communicate complex processes in a simplified manner. By illustrating tasks, decisions, and flows, BPMN facilitates better analysis and improvement of processes. Understanding these symbols is essential for anyone involved in process mapping comparison.
To begin with, BPMN consists of different elements, including tasks, events, gateways, and flows. Each of these plays a unique role in depicting the process. Tasks represent activities, while events indicate occurrences that affect flow. Gateways illustrate decision points, guiding how the process branches or converges. Lastly, flows connect all elements, showing the sequence and progression. Mastering these basics empowers teams to create effective BPMN diagrams, leading to enhanced communication and improved business outcomes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of BPMN
BPMN, or Business Process Model and Notation, presents various advantages and disadvantages. One of the key advantages is its standardized nature, allowing stakeholders to understand the processes without extensive training. This visual representation enhances clarity and communication, making it easier to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Furthermore, BPMN supports complex processes, accommodating various workflow scenarios, which aids in process mapping comparison across different methodologies.
However, BPMN also has drawbacks. Its complexity can overwhelm users unfamiliar with the notation, leading to misinterpretations. Additionally, while it excels at detailing processes, BPMN does not inherently capture qualitative aspects of business processes, such as team dynamics or organizational culture. These limitations can hinder its effectiveness in certain scenarios, serving as a point of consideration when choosing the best process mapping methodology. Ultimately, weighing these advantages and disadvantages is essential for organizations looking to enhance their process mapping efforts effectively.
Process Mapping Comparison: Specialized Methodologies
Process Mapping Comparison focuses on how various specialized methodologies can influence organizational processes. Each methodology presents unique features and frameworks that cater to specific business needs. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the best approach to optimize workflow efficiency and performance.
There are several methodologies worth considering, including Value Stream Mapping, SIPOC Diagrams, and Swimlane Diagrams. Value Stream Mapping identifies key value-added steps in a process, enhancing overall productivity. SIPOC Diagrams visually outline Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers, providing a comprehensive view of operations. Swimlane Diagrams clarify roles and responsibilities across departments, illustrating where tasks overlap or diverge.
By analyzing these specialized methodologies in-depth, organizations can better align their processes with strategic objectives. A clear understanding of process mapping allows for improved efficiency, facilitating timely decision-making and resource allocation. Ultimately, adopting the right methodology can lead to significant improvements in both performance and customer satisfaction.
SIPOC Diagrams
SIPOC diagrams serve as a powerful tool in process mapping comparisons. They provide a structured way to visualize the elements that constitute a process, focusing on Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers. By outlining these components, stakeholders can better understand the entire workflow, making it easier to identify areas for improvement.
The design of a SIPOC diagram begins with defining the process in question, mapping out the inputs and outputs that are essential for successful operation. Next, identifying suppliers and the customers impacted by the process allows for a comprehensive view. This methodology not only helps clarify the steps involved but also engages all relevant parties. Ultimately, SIPOC diagrams enhance communication and ensure that everyone involved has a mutual understanding of their roles, contributing to effective process mapping and management.
Basics of SIPOC Diagrams
SIPOC diagrams are vital tools for process mapping comparison, providing a high-level overview of a process’s essential elements. The acronym SIPOC stands for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers. By structuring a process visually, these diagrams help teams identify critical components, ensuring everyone understands the process flow from start to finish.
When creating a SIPOC diagram, first identify the suppliers that provide inputs for the process. Next, list the inputs necessary to achieve the desired outputs. The central block represents the main process steps, which culminate in outputs delivered to customers. Finally, defining the end customers establishes the purpose and importance of the entire operation. By utilizing SIPOC diagrams, teams can effectively compare processes, leading to improved efficiency and a clearer understanding of interrelated elements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SIPOC Diagrams
SIPOC diagrams are valuable tools in process mapping comparisons, offering clear insights into a process’s landscape. One advantage is their ability to provide a high-level overview, showing suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers. This clarity helps teams quickly understand the scope and key elements of a process, fostering better communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
However, SIPOC diagrams also come with limitations. They may oversimplify complex processes, neglecting important details that can impact decision-making. Additionally, crafting an effective SIPOC requires significant input from team members, which can be time-consuming and tedious. Balancing the simplicity of a SIPOC with the need for thoroughness is essential to maximizing its benefits while minimizing drawbacks. Teams should consider these factors carefully to optimize their process mapping efforts.
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts serve as an invaluable tool in project management, illustrating the schedule and progress of tasks over time. They consist of horizontal bars where each bar represents a task anchored on a timeline. This visual representation allows team members to easily grasp which tasks are active, their duration, and how they overlap with other activities.
One of the key advantages of using Gantt charts in process mapping comparison is their ability to highlight dependencies between tasks. When tasks are interrelated, it’s crucial to manage their timing effectively to avoid delays. With Gantt charts, you can assess how any change or delay in one task might impact others, ensuring a smoother workflow. Furthermore, the straightforward layout of Gantt charts makes it easier for stakeholders to monitor progress, facilitate adjustments, and align resources effectively throughout the project.
Read: How to Create Journey Maps From Transcripts
Basics of Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are essential tools for process mapping, offering a visual representation of project timelines and task management. By displaying tasks along a timeline, these charts help teams understand dependencies and allocate resources efficiently. Gantt charts break down complex projects into manageable parts, allowing stakeholders to visualize progress and deadlines at a glance.
One key aspect of Gantt charts is their ability to enhance communication among team members. By updating the chart, everyone can easily track task completion and identify potential bottlenecks. Additionally, Gantt charts facilitate planning by allowing teams to set realistic timelines and adjust as necessary. Ultimately, these charts are vital in process mapping comparison, as they provide clarity and structure to project management, ensuring that all team members are aligned towards the same goals.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gantt Charts
Gantt charts offer several advantages in process mapping. First, they provide a clear visual representation of project timelines, making it easier to monitor progress at a glance. This clarity can enhance team collaboration by clearly showing who is responsible for each task and when it’s due. Additionally, Gantt charts allow for effective resource allocation, as managers can identify overlapping tasks and ensure that team members are not overloaded.
However, there are also disadvantages associated with Gantt charts. One significant drawback is their complexity, especially for large projects with many interdependent tasks. Creating and maintaining an accurate Gantt chart can be time-consuming and may require specialized software. Furthermore, Gantt charts can oversimplify projects by failing to capture the nuances of tasks that may not follow a linear path, potentially leading to miscommunication among team members.
In sum, while Gantt charts can be valuable tools for process mapping comparison, one must weigh their advantages against the potential downsides before implementation.
Extract insights from Customer & Employee Interviews. At Scale.

Conclusion: Choosing the Right Process Mapping Methodology
Selecting the appropriate process mapping methodology can significantly enhance your project’s effectiveness. With various methodologies available, it’s essential to evaluate each one based on your specific needs and goals. Whether you are considering a straightforward flowchart or a more complex SIPOC diagram, understanding their unique strengths will guide you toward the best option.
In a process mapping comparison, consider factors like the complexity of your processes, stakeholder involvement, and the desired clarity of communication. Engaging relevant team members throughout the selection process can facilitate valuable insights, ensuring the chosen methodology aligns with both the organization’s culture and the project objectives. Making an informed choice can lead to clearer processes and better overall outcomes.
Key Takeaways from Process Mapping Comparison
When conducting a process mapping comparison, several key findings emerge that can significantly enhance your understanding and application of different methodologies. Firstly, each process mapping technique offers unique advantages and caters to specific project needs. For instance, some methodologies excel in visual representation, allowing users to quickly understand complex data, while others focus on analytical depth, highlighting critical trends and insights.
Secondly, the time investment required for each process mapping approach can vary greatly. Some methods are more straightforward and less time-consuming, while others may provide more detailed analysis but necessitate a steeper learning curve. This understanding allows organizations to weigh their options based on available resources and project goals. In conclusion, a thoughtful process mapping comparison can empower teams to choose the most suitable methodologies for their specific objectives, ultimately driving better outcomes.
Recommendations for Different Business Needs
When considering a Process Mapping Comparison for different business needs, it’s essential to identify the specific requirements of your organization. Different process mapping methodologies serve distinct purposes, which can impact the effectiveness of your business operations. For example, if your focus is on improving customer service interactions, Flowcharts may offer a clear and straightforward visualization of the process. Conversely, if you need to analyze complex systems, BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) can provide greater detail and clarity.
To ensure you select the best methodology, consider the following factors: the complexity of your processes, your team’s familiarity with various methodologies, and the specific outcomes you desire. By aligning your choice of process mapping with these considerations, you can enhance understanding and communication across your organization, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and performance.







